Research in fields surrounding cognitive science is providing increasing evidence that understanding of representations is formed in a dialectic between the social and the neural. Such research opposes the stratification of neural, cognitive, and social layers in the manner of the stratification of transistors, machine languages, and software applications in computer engineering. For example, researchers in conversation analysis (Garfinkel & Sacks, 1970; Goodwin & Heritage, 1990) have shown that the creation of meaning is changed in social interaction by split-second variations in conversational turn-taking. This argues for a rather direct relation between social interaction and neural organizations. Similarly, neurobiologists have recently undermined the plausibility of explaining perception by storage and retrieval of sense impressions; rather "memory" is a production of perceptual activity and motor activity that coordinates the present interaction by recomposing previously activated neural processes (Edelman, 1987; Freeman, 1991; Maturana, 1983). Crucially, the internal, neural processes that control perception are themselves organized by the ongoing social and physical activity (Bartlett, 1932; Dewey, 1896; Rosenfeld, 1988).
This research raises theoretical, methodological and practical issues for educators and psychologists who are concerned with how students learn scientific concepts. We illustrate these issues with a case study of science learning. The learners begin with a doubly uncertain experience: They are uncertain about what aspects of motion to see and about how to express the relationship that links vector notation to motion. Through shared activity, students are able to construct a way of meaningfully seeing, notating, and communicating about motion. We show that social and neural processes mutually constrain student's learning.
For example, consider this statement, which was seen on a postcard : "Gravity: It's not just a good idea, it's the law." This humorous slogan overlays two meanings of "law," legislative and scientific. These two different meanings are ordinarily not in contradiction because these meanings are localized in different communities of practice. However, when both practices are simultaneously invoked, interpretation is uncertain (and perhaps funny).
As in the case with the lawyer and the scientist, a deep contradiction of perspectives occurs when students learn physics: Everyday understanding of motion often contradicts scientific understanding. Research on student's understanding of scientific concepts finds significant differences between students' and scientists' interpretations of concepts like "acceleration," "energy," and "force" (Confrey, 1990; Halhoun & Hestenes, 1985; McDermott, 1984). But the differences between students and scientists are not necessarily localized at the level of concepts. To continue the analogy, an attorney cannot become a scientist simply by changing her definition of law; neither should we expect a student to become a scientist simply by changing her definition of "acceleration." Differences in perspectives extend throughout the fabric of thinking, including perception, focus of attention, descriptions of the world, and practices of interaction with the world. Thus, learning science (or any other discipline) requires crossing a large gap in perspective and practice; it requires becoming a member of a community of observers that sees and acts in ways that are at first incomprehensible or imperceptible to a newcomer. Put succinctly, learning science is a process of enculturation.
The case study that follows exemplifies each level within our framework. We provide excerpts from two students' behavior over the course of one hour. We do so to make two points. First, we call attention to the fact that basic impasses and learning events which occur in science education, even those occurring within a single hour of instruction, require analyses at each of these levels. Second, we argue that basic research on learning at these levels must examine social and neural organizations in an integrated fashion.
Our case study illustrates these levels as follows: We start with the issue of constructing mutual intelligibility of social action in a very local context. This involves acting on and re-perceiving materials (Bamberger & Schön, 1983) as well as displaying, confirming and repairing social meanings of these actions (Clark & Schaefer, 1989). We next move to the issue of building shared ways of interpreting a notation. The issue is generating a shared understanding of the relationship between the configuration (form) of the notation and consequent activity. Students acheive this understanding by negotiating a relationship of communicative metaphors to experience (Roschelle, in press; Schön, 1987). Finally, we suggest that the goal of learning is not just to make experience meaningful in a personal way. People learn to become a member of a community (Lave & Wenger, 1989). This requires simultaneous, coordinated changes to one's ways of seeing, talking, and acting.

|
|
|
|
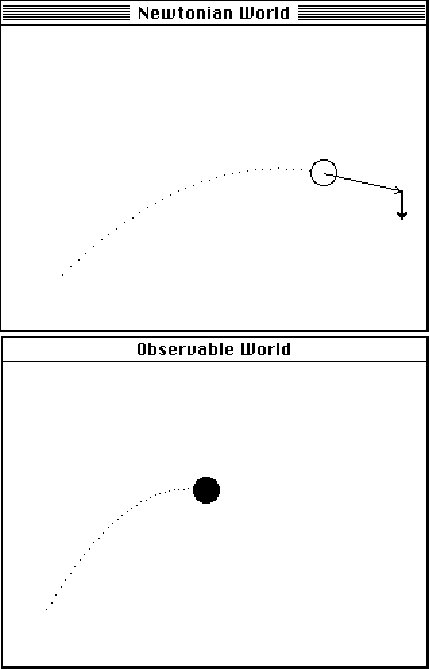
 |
Gerry and Hal are trying to replicate this motion, which appears in the Observable World window. | |
| G: And I think the angle should be pointing downwards, or else |
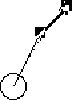 |
To produce the motion, Gerry suggests changing the direction of one
of the arrows.
The thin arrow is velocity. The thick arrow is acceleration. |
| H: Down?
G: Yeah, or else H: Like this? |
 |
Hal indicates uncertainty, and asks for confirmation. Then apparently unsatisfied with the confirmation, Hal initiates a clarification, using the mouse to demonstrate his current interpretation. |
| G: No. Um, that angle I think is OK, |
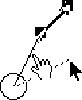 |
Gerry initiates a repair, first by indicating that he was not talking about velocity. He touches the velocity to make this clear. |
| G: But the fat an-, the fat arrow should be pointing downwards |
 |
Gerry continues the repair by presenting the correct interpretation, he wanted the acceleration arrow pointed downwards. Again he touches the arrow. |
| H: Like this?
G: Yeah. |
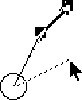
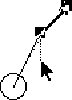 |
Hal uses the mouse to ask for clarification, this time dragging
the acceleration vector down.
Gerry confirms. |
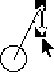 |
Hal completes the transaction by releasing the acceleration. |
Figure 2: Negotiating the Meaning of Terms
Hal's actions with the mouse show that he intends to move the velocity in the upwards direction, while Gerry is talking about the acceleration. Therefore, Hal cannot coordinate the meaning of Gerry's utterance with the meaning of the action he is in the process of undertaking. As a consequence, a breakdown occurs, signalled by Hal's identification of one of the incoherent elements in the on-going activity ("down?"). Importantly, the form this breakdown takes is an invitation for Gerry to enter into the eye-hand coordination loop. That is, Hal adjusts his active motion with the mouse to coordinate with Gerry's verbal description of down, and asks Gerry, "Like this?"
Gerry accepts the invitation by simultaneously producing a verbal repair ("No, not this, but that") and an example of the movements he wishes Hal to undertake. Gerry's gestures, even without the talk, project a suggestion to "Put that back. Pick up this and make it point downward." This combination of verbal repair and gestural suggestion is apparently effective, for Hal returns the velocity arrow to its original location, and begins a new hand-eye coordination that pulls the acceleration arrow into perceptual conformity with the students' sense of "down." Again, this coordination is opened up for social negotiation between Gerry and Hal ("Like this?" "Yeah.") This time Gerry and Hal agree.
This example suggests that mutual intelligibility succeeds in the EM situation because the tool offers opportunities for social negotiation to become a part of perception-action feedback loops. Mutual intelligibility is a consequence of the tight coupling of social and neural processes, such that the action-reaction loop between the people and the physical materials is coherent and unified.
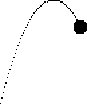
In the episode reproduced in Figure 3, the students have succeeded in
reproducing the goal parabola exactly, but only through trial and error.
Preceding this conversation, neither student has explained the relationship
between the setting of the arrows and the resulting motion. During the
interaction shown here, Gerry and Hal use a combination of talk, gesture,
and activity to come to a better understanding of the notation. They point
to objects to make references clear, gesture and act out concepts, and
synchronize their talk to events on the computer screen. The students collaboratively
construct an understanding of what the particle notation is and how it
works. Roschelle & Behrend (in press) have described this process as
the construction and maintenance of a "joint problem space."
|
|
|
|
| G: It [acc] stays the same, but it influences the long arrow
[vel]
H: I still- I don't understand what it's doing. [bracketted nouns inserted based on gestures and display] |
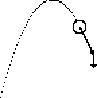 |
Gerry now sees acceleration as a change ("influence") on velocity.
Hal is watching the same display, but apparently does not see this relationship.
The discourse problem for this episode is for Gerry to communicate his understanding to Hal. |
| G: OK, I think. See, it [acc] pulls it [vel] down
H: mm,hmm. |
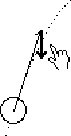 |
Gerry re-iterates his view of acceleration as change in velocity, this
time using the metaphor of acceleration as a pull on velocity. He uses
gestures to act out the pulling he is describing, integrating the idea
in his talk with the same idea expressed in gesture.
Hal indicates his attention. |
| G: so it [acc] makes this [vel] shorter
H: Oh:::right G: cause that'll slow it down. |
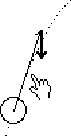 |
Gerry applies this view to the present circumstances: acceleration
makes the velocity shorter, explaining why the motion gets slower. He points
to the velocity as he talks to clarify which arrow gets shorter.
Hal indicates a partial understanding. |
| G: And also
H: as it pulls it G: the long arrow's [velocity is] pointing this wayG: so this one's [acc] pulling it [vel] down H: so it's [acc] pulling it [vel] downward G: so it [acc] will pull the angle [direction of vel] down H: right. |
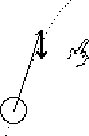 |
Gerry continues applying his view, explaining the change of direction
of velocity. As he does so, he moves his finger analogously to the change
in velocity.
By completing the consequent sentence jointly with Gerry, Hal shows that he has understood the explanation. |
| G: so then
H: there you go right there |
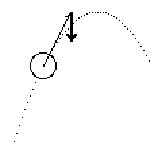 |
Gerry now starts the simulation running, and starts to talk over the
simulation.
Hal interrupts to indicate that he now sees the processes Gerry described above. |
| G: it [vel] crosses [the horizontal] |
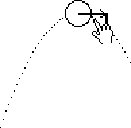 |
Gerry continues the story, synchronizing it to the running simulation; the change in velocity eventually results in the direction of velocity becoming horizontal. |
| G: and then it [acc] pulls it [vel] down.H: yeahG: and makes the angleH: Its kind of like a weight or something. |
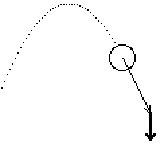 |
…and finally pointing downwards, completing the parabola. His final
sentence is timed to correspond to the downwards motion of the particle.
Hal indicates his understanding of the explanation by paraphrasing it in his own words. |
During the interaction shown in Figure 3, Hal moves from "not understanding what it is doing" to interpreting the bold line as "kind of like a weight or something." That is, the bold line becomes a representation for Hal; it is a form that stands for something else.
To understand the significance of this episode, it is necessary to understand some general aspects of the problems that students encounter while trying to interpret the EM notation. First, students often do not notice important attributes of the display, or misinterpret their significance. In particular, many students do not notice that the velocity arrow changes over time. Hal had not noticed this before the conversation in Figure 3. Similarly, students often misinterpret the significance of properties. For example, students sometime decide that where the velocity arrow points is significant; they expect the velocity to point to the apex of the parabola, and ignore the significance of velocity as initial speed and direction. The list of unusual ways that students perceive the screen is very long (Roschelle, 1991).
Second, students build explanations by applying metaphors to the situation (Roschelle, 1991). In this example, as in many successful explanations, the "pulling" metaphor is used. Pulling is a good metaphor because it approximately captures the relation between acceleration and change of velocity. But many other metaphors occur to students: guiding, stretching, attracting, and balancing (Roschelle, 1991). Thus, the situation is doubly indeterminate for students; they are not sure what they should be noticing, and they are not sure what metaphors might be useful in structuring their experience.
Consider Gerry and Hal's conversation apart from the display. Read as a separate text, the conversation appears as meaningless gibberish. Where does the significance of this discussion arise? A close look at the data suggests that it arises through the exacting coordination of the students' perceptions of the running simulation, their gestures in front of the display, and their conversational interaction. In this dialog, Gerry invited Hal into his active process of perceiving-describing-and-looking — Gerry produced descriptions and gestures that primed Hal's attention for those features he should look for next in the changing display. Thus, Gerry's social actions oriented Hal's perceptual processes. Through this coupling, Hal came to re-perceive the simulation as Gerry does; that is, Hal notices the change in velocity over time and its relation to the speed and direction of motion.
At the same time, Gerry and Hal used the "pulling" metaphor to express relationships between the notation and the resulting motion. In particular, Gerry used "pulling" three times in a row: First he connected the present state of the simulation to the past state, then to the next state, and eventually to the final direction of motion as the particle left the display. As he did so, Hal slowly came to use the metaphor as Gerry did. He started by indicating his attention, then a partial understanding, then he articulated the basic mechanism ("it pulls it") and then the mechanism and its consequence ("so it's pulling it downwards"). As additional data (presented in Roschelle, 1991) shows, Hal's explanation eventually came to be quite close to a physicist's qualitative description of acceleration. Thus, the sharing of the significance of the notation occurred through close coupling of social and perceptual levels of organization in the students' collaborative activity.
In the interview following the session, Hal explicitly mentioned his difficulty in mapping his (rudimentary) knowledge of physics to the EM:
H: I'm trying to understand, um, exactly
E: What's that?
H: Nothing, I'm just trying to understand what this has to do with, uh, I mean if there's anything I can- not- I know it has a lot to do with physics but, I'm just trying to understand um- Trying to see if I can think of any um- doesn't matter
E: No, it does matter. What?
H: No just, you know, you know I'm trying t- I mean I don't know anything about physics but you know I've heard about it
E: mm, hmm.
H: Heard about certain things and I'm just trying to sort of see what law of physics- what anything I've heard, anything that has anything to do with this.
Neither Hal nor Gerry were successful in making meaningful connections to physics concepts on their own.
The de-briefing interview following the Gerry and Hal's session can
provide a glimpse into the process of adopting the scientific community's
perspective and conventions (Figure 4). In this interview, the experimenter
explained the mapping of the scientific terms "velocity" and "acceleration"
onto the two arrows of the EM display, and how this mapping differs from
everyday usage of these terms. In response, the students spontaneously
applied these terms to describing the behavior of an automobile. Interestingly,
the students correctly applied the concept of acceleration to situations
other than "speeding up." This marks significant progress in moving from
an everyday perspective to a scientific one. Whereas an everyday perspective
sees speeding up, braking, and turning as three characteristically different
events, a scientific perspective sees these events as different manifestations
of the same underlying description. The students' uniform explanation of
all three events is a significant step towards participation in the scientific
perspective.
|
|
|
| E: Now in physics, what these arrows would be called is the thin arrow
would be called velocity
H: Uh, huh. E: and velocity means both speed and direction H: Yeah E: And the thick arrow would be called acceleration, and acceleration in physics means change in velocity. H: Ohhh. E: So the thick arrow tells you how the thin arrow changes |
Experimenter explains the mapping of the scientific terms "velocity" and "acceleration" onto the thin and thick arrows respectively. |
| H: Oh so like you're in a car, and you slap on the gas petal
E: Mm, hmm. H: And you're going at a certain speed, but you slap on the gas pedal, and you start to go faster. G: It would be like an arrow, a thick arrow [acc] going out in front of your car |
Hal introduces topic of a car accelerating.
Gerry makes the mapping to the EM simulation, that the acceleration vector would be directed forward. |
| E: And what about when you put on the brakes?
H: When you put on the brakes its like the arrow [acc] coming back in towards the car and slowing it down. |
Hal correctly describes braking as acceleration in the opposite direction as the car's motion. |
| E: Hmm, mm. Now I'll ask you a tricky one. What happens when you go
around a curve?
H: Ho:::::. G: That's like your steering has changed, so its like the thick arrow [acc] is pointing around the curve and it sort of drags your car hhhh. ((laughter by all)) E: Suppose you're turning to the right, is the thick arrow to the right or left? G: Thick arrow would be to the right. H: If you're going to the right. Yeah. |
Both correctly describe the acceleration vector for the car going around a curve as pointed in the direction of the turn (in this case, toward the right). |
Although the students did not use the EM display directly during this conversation, the objects of the display still served as important common ground between the students and the experimenter. In particular, the available shared understanding of the meaning of "thick arrow" and "thin arrow" enabled the students and the experimenter to discuss the students' knowledge. In general, it will take many small episodes like this to guide students into the scientific community's way of solving problems and talking about them. Without a rich, perceptual common ground (provided in this case by the computer display), it is difficult for students and scientists to recognize and repair their differences in belief, language, and perspective.
We believe that the problems addressed at each unit of analysis are fundamental to science education. Students need to be able to track the local progress in a learning activity. They need to grasp the significance of scientific notations. They need to learn to use scientific notations the way that the scientific community does. Thus the specific process of learning scientific concepts, at each level, must be accountable to the overall demands of shared activity. This in turn, requires an analysis of scientific concept learning which is compatible with a view of science learning as enculturation.
Enculturation poses basic theoretical issues about representation and meaning: How can one learn to perceive aspects of the world that are invisible within one's current world view? For example, a physicist sees deformation and resilience in every real object (even a glass marble), whereas everyday folks see the world as composed of rigid entities (diSessa, 1987). How can one learn meanings that are both more complex and dramatically at odds with one's current meanings? For example, Maxwell's laws require that electricity communicates information at the speed of light while the electrical particles which carry information move only at a slow drift; to many students this is incomprehensible, and it is certainly more complex than familiar physical behaviors (Haertel, 1987). Considering science learning as enculturation immediately brings the reflective educator face to face with these questions, as well as any number of related forms of the learning paradox (Bereiter, 1985).
From a cognitive standpoint, the learning paradox rapidly degenerates into a reductio ad absurdum. The only apparent cognitive way to treat enculturation from one world view to another is to define a universal perception of microfeatures, or microcategories. Similarly, one must define universal atomic meanings. From these microfeatures and atomic meanings, one can attempt to construct a translation of one paradigm to another. For example, most schema-based theories of learning claim that representations come from other representations, by a process of refinement, generalization, and composition (Chi, Glaser & Farr, 1988; Norman, 1982). Data to be represented is expressed as programmer-supplied primitive categories and measurable features. Schema-based models assume that the world comes pre-represented, already parameterized into objects and features. Since the world can be modeled as objective fact, building in primitive features into the model is viewed as just bootstrapping the program. Researchers may ask, "What is the raw material of reasoning?" (Koedinger and Anderson, 1990), but they tend to give one choice —varieties of representations. Schema models of learning involve perceptible features, but deal only with a priori representations of experience (Schank and Abelson, 1977).
To do so is to commit what Dewey (1926) termed "The Philosophical Fallacy." This fallacy occurs when one assumes the necessity of a more detailed and complex underpinning for an earlier developmental stage to explain the emergence of later stage (Tiles, 1988). In schema theories of science learning, this occurs because detailed and complex categories and microfeatures must be built into the initial state of the system for learning to occur. Moreover, rather than merely supporting everyday qualitative, inaccurate reasoning about physical world, the categories and microfeatures must be compatible with more stringent demands of precise scientific reasoning.
Accepting that science learning is enculturation forces the opposite assumption, that little if anything is sensible to students as they begin to learn science. Students neither see the same phenomena, nor have meanings for the fundamental concepts that scientists use. Indeed, students start out with very few distinctions in areas that are richly textured for the experienced physicist—for example, the description of motion. Moreover, their theoretical vocabulary has concepts that are less specific and less general. Thus, there is no universal set of microcategories upon which scientific explanation can be bootstrapped (Gregory, 1988).
However, if one moves from a pure cognitive standpoint to a socio-neural standpoint, the learning paradox need not occur. As Iran-Nejad (1990) points out, a social-neural standpoint overturns the basic assumptions in the pure cognitive story that give rise to the learning paradox. Neural research emphasizes viewing memory as dynamic, transient structures that are continually reproduced (Bickhard and Richie, 1983). At the level of neural architecture, the formation of new categories looks more like chaotic settling into a new activation state, rather than incremental modification of existing structures (Freeman, 1991; Edelman, 1987; Iran-Nejad, 1990). Thus the emergence of new categories is a matter of re-using transient organizations of neural maps; structured cues from the physical and social world gradually can stabilize new relations of features and world. Crucially, these maps coordinate perception and action—they do not represent how behavior or the world appears to an observer (Clancey, 1991). In addition, neural research emphasizes diverse sources of relational coordination, rather than just a strong central executive (Rosenfield, 1988). Through these sources, interaction can serve as a source of control for organizing new complexes of experience.
Social structures are critical for understanding how reproduction of existing scientific concepts can occur (Vygotsky, 1978). Considerable research has been done on the social processes by which conversational partners locally manage the uncertainty of meaning in a conversation (Clark & Schaefer, 1989; Goodwin & Heritage, 1990; Levinson, 1983). These processes enable conversational partners to seek convergence in meaning and repair divergences. Similarly, students construct the meaning of tasks, goals, and means in social activity, creating a "construction zone" (Newman, Cole & Griffin, 1989) or a "Joint Problem Space" (Roschelle & Behrend, in press).
Learning how a community uses certain notations and meanings generally involves a process in which members of the community can participate with learners in joint activity (Lave & Wenger, 1989). The use of particular notations and their meaning can thereby be negotiated relative to (1) the conventions of the community and (2) the shared experience at hand. Thus, we have argued that basic problems at the levels of mutual intelligibility, activity structures, and communities of practice can only be resolved by simultaneously drawing on stable relations of social and neural organization. Put simply, a learner participates in the creation of what is to be represented and what constitutes a representation by simultaneously perceiving, acting, and communicating. Coherence, composition, and coordination among neural and social processes are the fundamental forces at work.
At the level of the significance of notations in activity, we draw attention to the richness of modalities available to students for perceiving and talking about meaning. In the specific examples we considered, one key aspect that students sought to understand was the relation between the arrow notation and changes of direction. To do so, they used gestures, metaphors, and experimentation with the simulation. As we pointed out earlier, these resources are essential—without them, Gerry and Hal's talk is gibberish. Indeed in actual scientific practice and in everyday talk, simultaneous use of multiple modalities of experience in close synchrony is a prominent fact. Yet, classroom science most often falls back on the manipulation of a single representational formalism, namely mathematics, as the basis for all learning. Thus designers should ask themselves, "How can I support a diverse ways of constraining meaning, both through experiential and social interaction?"
Finally, at the level of communities of practice, computer simulations and other instructional displays can play a significant role in learning because often there is no periphery in which newcomers can directly begin to participate in the work of the community. This is the case with air traffic controllers—there is no periphery in which common folk can practice the skills of guiding aircraft. A solution to this problem is the construction of animated microworlds, which provide activities in which newcomers can participate without danger or excessive expense. Of course, the validity of a microworld depends on getting the appropriate abstraction and simplification of the full-scale practice, especially the social interaction, which is often left out. For example, a paper and pencil simulation of air-traffic control may be so distant from the reality of the workplace that it is virtually useless in enabling newcomers to enter the professional community.
Our viewpoint differs from the usual stance of cognitive science. Cognitive science has most frequently taken a correspondence view of representation, a retrieval view of memory, and an individualistic view of meaning. These views minimize the need to consider social and neurological processes jointly. For example, in his recent proposal for a unified theory of mind, Newell (1990) places social and neural considerations outside the bounds of what he termed "The Knowledge Level"—the place of representation and knowledge in cognitive architecture. Newell places the "social band" on a time scale of hours and minutes, claiming it was not relevant to understanding the millisecond-based processing of the brain. Newell also places the neural-perceptual mechanism outside the scope of cognition, claiming perception to form a generic encoding substrata for the physical symbol system. Thus Newell relegates neural and social levels to the implementation and application of reasoning.
This model of learning misses much of the phenomenology of how representations are created, given meaning, and used. Science learning requires simultaneously perceiving new forms, generating new actions, and communicating new meanings. By requiring representation of categories and microfeatures prior to physical and social interaction, cognitive science has produced a view of learning that is incompatible with enculturation. Representing is, in essence, coordinating perception with action; this coordination takes place in a dialectic between the social and neural processes.
Bartlett, F. C. (1932/1977). Remembering-A study in experimental and social psychology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Reprint.
Bereiter, C. (1985). Towards a solution of the learning paradox. Review of Educational Research, 55, 201-226.
Bickhard, M. H. and Richie, D.M. (1983). On the nature of representation: A case study of James Gibson's theory of perception. New York: Praeger Publishers.
Chi, M.T.H., Glaser, R., & Farr, M.J. (Eds.) (1988). The Nature of Expertise. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Clancey, W.J. (1991). The frame of reference problem in the design of intelligent machines. In K. VanLehn (Ed.), Architectures for Intelligence, Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum .
Clark, H.H. & Schaefer, E.F. (1989). Contributing to discourse. Cognitive Science, 13, 259-294.
Confrey, J. (1990). A review of the research on student conceptions in mathematics, science, and programming. Review of Research in Education.
Dewey, J. [1896] (1981). The reflex arc concept in psychology. Psychological Review, III:357-70, July. Reprinted in J.J. McDermott (ed), The Philosophy of John Dewey, Chicago: University of Chicago Press, pp. 136-148.
Dewey, J. (1926). Experience and nature. Chicago: Open Court.
diSessa, A.A. (1987). Towards an epistemology of physics (Institute for Cognitive Studies Tech. Rep. No. 48). Berkeley, CA: University of California.
Edelman, G.M. (1987). Neural darwinism: The theory of neuronal group selection. New York: Basic Books.
Freeman, W.J. (1991). The physiology of perception. Scientific American, (February), 78-85.
Garfinkel, H. & Sacks, H. (1970). On formal structures of practical actions. In J.C.McKinney & E.A. Tiryakian (eds), Theoretical Sociology. New York: Appleton Century Crofts, 338-366.
Goodwin, C. & Heritage, J. (1990). Conversation Analysis. Annual Review of Anthropology, 19, 283-307.
Gregory, B. (1988). Inventing reality: Physics as language . New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Haertel, H. (1987). A Qualitative approach to electricity (Technical Report No. IRL-87-0001). Palo Alto, CA: Institute for Research on Learning.
Halhoun, I.A., & Hestenes, D. (1985). The initial knowledge state of college physics students. American Journal of Physics, 53, 1043-1055.
Iran-Nejad, A. (1987). The schema: A long-term memory structure or a transient functional pattern. In R. J. Tierney, Anders, P.L., and J.N. Mitchell (Eds.), Understanding readers' understanding: Theory and practice, Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Koedinger, K. R., & Anderson, J. R. (1990). Abstract planning and perceptual chunks: Elements of expertise in geometry. Cognitive Science, 114(4), 511-550.
Lave, J. (1988). Cognition in practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lave, J. & Wenger, E. (1989). Situated learning: Legitimate peripheral participation (Report No. IRL-89-0013). Palo Alto, CA: Institute for Research on Learning.
Levinson, S.C. (1983). Pragmatics. New York: Cambridge.
Maturana, H. R. (1983). What is it to see? ¿Qué es ver? 16:255-269. Printed in Chile.
McDermott, L.C. (1984). Research on conceptual understanding in mechanics. Physics Today, 37, 24-32.
Newell, A. (1990). Unified theories of cognition. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Newman, D., Griffin, P, & Cole, M. (1989). The construction zone: Working for cognitive change in school. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Norman, D.A. (1982). Learning and memory. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Roschelle, J. (in press). Learning by collaborating: Convergent conceptual change. Journal of the Learning Sciences.
Roschelle, J. (1991). Students' construction of qualitative physics knowledge: Learning about velocity and acceleration in a computer microworld. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of California, Berkeley.
Roschelle, J. & Behrend, S. (in press). The construction of shared knowledge in collaborative problem solving. To appear in O'Malley, C. (Ed.) Computer supported collaborative learning. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Rosenfield, I. (1988). The invention of memory: A new view of the brain. New York: Basic Books.
Schank, R. C., & Abelson, R. (1977). Scripts, plans, goals and understanding. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Schön, D.A. (1979). Generative metaphor: A perspective on problem-setting in social policy. In A. Ortony (Ed.), Metaphor and thought. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Tiles, J.E. (1988). Dewey. London: Routledge.
Vygotsky, L.S. (1978). Mind in society. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Press.