 |
University of Southampton Institute of Transducer Technology |
Polymer Thick-Film Sensors on Silicon |
Polymer-PZT composites
A new thick-film printable polymer-PZT composite paste has been developed in our laboratories. The paste is comprised of PZT (lead zirconate titanate) grains of an average 6 micron size dispersed in commercial thick-film polymer dielectric pastes (fig. 1). A capacitor structure (fig. 2) is used to test the piezoelectric activity of the paste. A force is applied on the sample and the charge generated is led to a charge amplifier. The value achieved till now is 14pC/N. The curing and poling of the paste has been optimised and currently we are investigating ways to improve the activity of the paste, which is already useable in sensor applications.

Figure 1 - SEM micrograph of the internal structure of the polymer PZT composite paste. The layers shown from top to bottom are: Ag-filled polymer paste, polymer PZT paste, Ag-Pd cermet paste, alumina substrate.
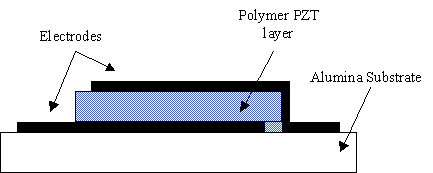
Figure 2 - Capacitor structure
Temperature and Humidity Sensors
The potential of using commercial pastes as sensor elements is investigated. Examples of a humidity and a temperature sensor are shown in figures 3 and 4 respectively.
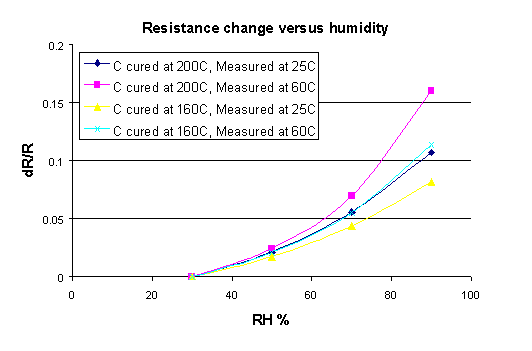
Figure 3. Change in resistance of carbon polymer pastes versus relative humidity
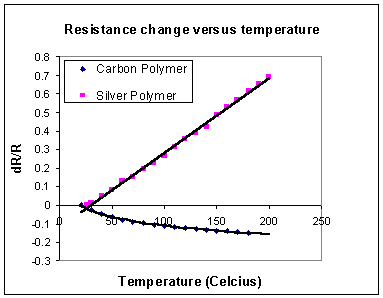
Figure 4. Change in resistance of silver and carbon filled pastes with temperature.
Polymer thick-film pastes on Silicon
Research is being done on printing polymer thick-film pastes on silicon substrates (fig. 5). Issues like adhesion, contamination, feature resolution, compatibility with silicon processing and accelerated ageing have been addressed. Further research on combining thick-film sensors with silicon integrated circuits is in progress.
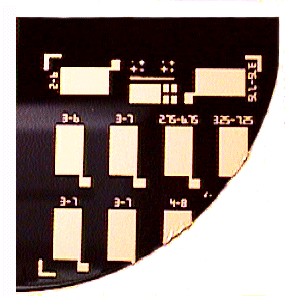
Figure 5 - Thick-film polymer patterns printed on Silicon substrate
|