Wednesday, September 27. 2006
Optimizing OA Self-Archiving Mandates: What? Where? When? Why? How?
We are so close to the adoption of Open Access Self-Archiving Mandates worldwide (with five of eight RCUK Research Councils plus the Wellcome Trust having already adopted them in the UK, the FRPAA proposing their adoption in the US, the EC Recommendation A1 proposing their adoption in Europe, at least 125 US university provosts expressing their support, and a number of individual universities and research institutions already adopting institutional self-archiving mandates of their own). This is the opportune time to think of optimizing the formulation of these mandates, so that they systematically interdigitate with one another to generate all of OA's target content, across institutions, disciplines, and nations worldwide, to confer the maximum of benefit in a minimum of time. A seemingly small parametric or verbal variant can make a vast difference in terms of the amount of OA a self-archiving mandate produces, and how quickly and reliably.
SUMMARY: With the adoption of Open Access Self-Archiving Mandates worldwide so near, this is the opportune time to think of optimizing how they are formulated. Seemingly small parametric or verbal variants can make a vast difference to their success, speed, and completeness of coverage:
What to mandate: The primary target content is the author's final, peer-reviewed draft ("postprint") of all journal articles accepted for publication.
Why to mandate self-archiving: The purpose of mandating OA self-archiving is to maximize research usage and impact by maximizing user access to research findings.
Where to self-archive: The optimal locus for self-archiving is the author's own OAI-compliant Institutional Repository (IR). (It is highly inadvisable to mandate direct deposit in a Central Repository (CR) -- whether discipline-based, funder-based, multidisciplinary or national. The right way to get OA content into CRs is to harvest it from the IRs (via the OAI protocol).)
When to self-archive: The author's final, peer-reviewed draft (postprint) should be deposited in the author's IR immediately upon acceptance for publication. (The deposit must be immediate; any allowable delay or embargo should apply only to the access-setting, i.e., whether access to the deposited article is immediately set to Open Access or provisionally set to Closed Access, in which only the author can access the deposited text; in either case, the article's metadata are immediately accessible webwide, allowing users to request eprint copies by email from the author immediately and semi-automatically during any embargo period).
How to self-archive: Depositing a postprint in an author's IR and keying in its metadata (author, title, journal, date, etc.) takes less than 10 minutes per paper. Deposit analyses comparing mandated and unmandated self-archiving rates have shown that mandates (and only mandates) work, with self-archiving approaching 100% of annual institutional research output within a few years. Without a mandate, IR content just hovers for years at the spontaneous 15% self-archiving rate.
WHAT: The primary target content is the author's final, peer-reviewed draft ("postprint") of all journal articles accepted for publication.Other contents are more than welcome too -- pre-refereeing preprints, research data, theses, book-chapters, etc. -- but let us not forget that peer-reviewed research is the primary target and raison d'être of the OA movement."The literature that should be freely accessible online is that which scholars give to the world without expectation of payment. Primarily, this category encompasses their peer-reviewed journal articles..." [Budapest Open Access Initiative]
(Only the final peer-reviewed draft need be deposited, not the publisher's proprietary PDF or XML, which should instead be linked, via a direct pointer to its URL or DOI on the publisher's website.)
WHERE: The optimal locus for self-archiving is the author's own OAI-compliant Institutional Repository (IR).That is the locus which, once mandated, will systematically scale up to cover all of research output space, worldwide. It is highly inadvisable to mandate direct deposit in a Central Repository (CR) -- whether discipline-based, funder-based, multidisciplinary or national. The right way to get OA content into CRs is to harvest it, via the OAI metadata-harvesting protocol, from the distributed OAI-compliant IRs. Not only should research institutions -- the primary research-providers -- mandate the self-archiving of their own researchers' output in their own institutional IRs, but research funders too should mandate that their fundees self-archive in their own institutional IRs. That is the most natural, universal and systematic way to reach 100% OA worldwide, and also the fastest and surest.
WHEN: The author's final, peer-reviewed draft (postprint) should be deposited in the author's IR immediately upon acceptance for publication.

The case for immediate access is exactly the same as the case for Open Access itself: otherwise research uptake, usage, impact, productivity and progress are needlessly delayed or lost. And in many fast-moving fields the "growth tip" for research progress is within the first 6-12 months from the time new results are available.
WHY: The purpose of mandating OA self-archiving is to maximize research usage and impact by maximizing user access to it.The motivation for the Open Access movement -- and hence for OA self-archiving by researchers and OA Self-Archiving Mandates by researchers' institutions and funders -- is to maximize research access in order to maximize research uptake, usage, impact, productivity and progress, for the benefit of research, researchers, their institutions and funders, and the tax-paying public that supports them and in whose interests the research is being conducted and published.
HOW: Depositing a postprint in an author's IR and keying in its metadata (author, title, journal, date, etc.) takes less than 10 minutes per paper.However, surveys show that only 15% of authors will self-archive unless it is mandated. Just requesting or recommending deposit does not work. Deposit analyses comparing mandated and unmandated self-archiving rates have shown that mandates (and only mandates) work, with self-archiving approaching 100% of annual institutional research output within a few years. Without a mandate, IR content just hovers for years at the spontaneous 15% self-archiving rate.
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Monday, September 25. 2006
125 Provosts For, 10 Against FRPAA Self-Archiving Mandate
SUMMARY: The actual impact of Open Access (OA) self-archiving on research, researchers, their institutions, their funders, and the tax-paying public (which has all already been shown to be highly positive) must be clearly separated from any hypothetical impact it might have on publishers (whether commercial or scholarly-society publishers). Researchers do not conduct research -- nor does the tax-paying public fund research -- for the benefit of publishers. The sole point at issue concerning the FRPAA is whether or not self-archiving should be mandated. The two concrete questions that researchers, their institutions and funders need to put to themselves regarding any "special relationship" with scholarly society publishers are therefore:
(a) Would (or should) researchers, their institutions and their funders knowingly choose to subsidise their scholarly societies with their own actual lost research impact in order to immunise those scholarly societies from any hypothetical risk of lost subscription revenue?
(b) If, contrary to all evidence to date, self-archiving were indeed destined one day to cause publisher revenue losses -- or even to force a shift to the open-access publishing cost-recovery model (with author-institutions paying the publication costs for their own institution's research output out of their own windfall savings from the cancellation of their former costs as user-institutions, buying in the published output of other institutions) -- is the prevention of that hypothetical outcome something that researchers, their institutions and their funders would (or should) knowingly choose to subsidise with their own actual lost research impact?
A dissenting minority of 10 US provosts opposes the FRPAA Self-Archiving Mandate (vs. 125 in favor) on the grounds of risk to scholarly society subscription revenue. There is obviously a biomedical publisher lobby behind some or all of the 10 dissenting voices; the arguments are old ones, already rebutted many times:
(1) The hypothesis that mandated self-archiving will force a shift to the OA publishing cost-recovery model is pure speculation at this time, with no evidence in its support, and evidence from both the American Physical Society and IOPP contradicting it.
(2) But even if the hypothesis were ever to come to pass, it would not mean "diminishing funds available for research to benefit the public good".
(3) To force a shift to the OA publishing cost-recovery model, there would first have to be substantial revenue losses for publishers, from institutional subscription cancellations.
(4) But for every penny of revenue lost by publishers in the form of institutional subscription cancellations, there has to be a penny saved by institutions, in the form of windfall savings.
(5) Hence if publisher revenue losses were ever to force a shift to the OA cost-recovery model, the institutions would have a large annual pot of windfall savings on which to draw to pay for their own outgoing publication costs.
(6) Hence there would be nothing at all "requiring authors to pay for their publications through their Federal grants, diminishing funds available for research to benefit the public good."
(7) It is only now -- when there are neither any institutional subscription cancellation pressures, nor any institutional subscription windfall savings -- that it looks as if paying OA publishing costs would require diverting money from research.
(8) Hence it is both self-serving and self-contradictory to invoke both the "damage" hypothesis and the "research fund diversion" hypothesis against the FRPAA in the same breath: If the hypothetical "damage" is the hypothetical subscription revenue loss, then that is also the diversion: no need to poach hypothetical research funds.
(9) The rationale for the FRPAA self-archiving mandate, however, has nothing to do with speculative hypothesizing about journal economics but with demonstrable facts about maximizing research usage and impact.
 Peter Suber has already provided an excellent critique of the letter from a dissenting minority of 10 US provosts who oppose the proposed FRPAA Self-Archiving Mandate (versus the other 125 provosts who support it):
Peter Suber has already provided an excellent critique of the letter from a dissenting minority of 10 US provosts who oppose the proposed FRPAA Self-Archiving Mandate (versus the other 125 provosts who support it):But one can never say enough in support of a good thing (and against a bad one!), so what follows below is a detailed, systematic, point-by-point critique of the dissenting provosts' position and the arguments adduced in its support.
It is fairly obvious that there is a biomedical publisher lobby behind some or all of these dissenting voices, since the statements of these 10 dissenting provosts (several of them members of executive committees of the American Physiological Society!) are almost a verbatim echo of the very same points that the publishing lobby has been making over and over, in trying to oppose self-archiving mandates worldwide [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], hence the accompanying press release from the American Physiological Society ["APhS"](not to be confused with the American Physical Society!) from which more will be heard below too [6, 7, 8].
(The attempted opposition to self-archiving mandates has already proven unsuccessful in the UK, where four of eight RCUK research funding councils have already mandated self-archiving, beginning October 1 2006.)
But never mind, we will take the points made in both the American Physiological Society press release and the letter from the ten provosts at face value:
On Fri, 22 Sep 2006, Martin Frank (American Physiological Society ["APhS"]) wrote:(If the $3 billion dollar figure is pertinent at all, then the first thing to call to mind is the more than $30 billion dollars in annual research investments of the 125 institutions that had expressed exactly the opposite concern...)
SENIOR ACADEMIC OFFICERS EXPRESS THEIR CONCERN ABOUT S.2695, THE "FEDERAL RESEARCH PUBLIC ACCESS ACT OF 2006"
(APhS): (Bethesda, MD) - September 22, 2006 - Senior academic officers from 10 institutions issued a letter to Senators John Cornyn (TX) and Joseph Lieberman (CT) expressing their concerns about the provisions of S.2695, the "Federal Research Public Access Act of 2006." These institutions, which collectively make nearly $3 billion in annual research investments, expressed their concerns that mandating a six-month public release of journal articles would negatively impact the academic community and the publishers that disseminate their work.
But let us look at this more closely, for on the face of it, the effect of making research Open Access has already been demonstrated to have a highly positive impact on its impact (sic) -- i.e., the degree to which it is accessed, used, and cited.
So now let us hear more about the alleged downside of this -- but let us be very careful to separate its actual impact on the academic community (which we already know to be positive) from its hypothetical impact on (some) publishers.
For, lest we forget it: researchers do not conduct research -- nor does the tax-paying public fund research -- for the benefit of publishers [9, 10, 11, 12].
(APhS): In signing the letter in opposition to S.2695, Dr. Robert Rich, Senior Vice President and Dean, University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicine, expressed his concern that "the legislation would damage the special relationship between scholarly societies and academic communities who work in partnership to ensure that these communities are sustained and extended, science is advanced, research meets the highest standards, and patient care is enhanced with accurate and timely information."The sole point at issue with the FRPAA is whether or not self-archiving should be mandated. All evidence so far shows that self-archiving enhances research impact. No evidence so far shows that self-archiving reduces scholarly society publisher revenues, and this has been explicitly confirmed by the two scholarly society publishers whose published contents have been self-archived the longest and the most, the American Physical Society and the Institute of Physics Publishing: They both report that they have detected no subscription losses as a consequence of self-archiving.
Nevertheless, some scholarly society publishers fear, despite the absence of any actual evidence, that self-archiving will cause "damage" if mandated by the FRPAA (and by other research funders and institutions worldwide). No one knows whether or when these fears of damage will actually come true, but let us agree that there is a non-zero risk for publisher subscription revenues here, and that it is definitely not outside the bounds of either logic or likelihood that universal availability of authors' final drafts could eventually generate cancellation pressure on subscriptions. Yet what needs to be done by the academic community is to weigh this hypothetical risk to publishers' subscription revenues against the demonstrated benefits to the research impact of researchers, their institutions, their funders, and the tax-paying public that funds them.
Hence there are two very concrete questions that researchers and their institutions and funders need to put to themselves regarding this "special relationship" with scholarly society publishers:
(i)Would (or should) researchers, their institutions and their funders knowingly choose to subsidise their scholarly societies with their own actual lost research impact in order to immunise those scholarly societies from any hypothetical risk of lost subscription revenue?
(ii) If, contrary to all evidence to date, self-archiving were indeed destined one day to cause publisher revenue losses -- or even to force a shift to the open-access publishing cost-recovery model (with author-institutions paying the publication costs for their own institution's research output out of their own windfall savings from the cancellation of their former costs as user-institutions, buying in the published output of other institutions) -- is the prevention ofthat hypothetical outcome something that researchers, their institutions and their funders would (or should) knowingly choose to subsidise with their own actual lost research impact?
(APhS): Rich also expressed concern that "S.2695 would divert scarce Federal dollars away from research in order to provide a service already provided to the public by society publishers."It is already a speculative hypothesis that self-archiving would damage subscription revenue; but it is wildly counterfactual to say that FRPAA is about diverting funds away from research in order to pay publishers!
FRPAA is not a mandate to convert to OA publishing: it is a mandate to convert to author self-archiving. FRPAA says nothing about diverting funding from research to publication.
The hypothetical long-term sequel of mandated self-archiving -- a conversion from institutional subscription-charges to institutional publication charges -- is merely speculation, in the absence of any objective supporting evidence (and in the face of counter-evidence). But even if the hypothesis were ever to prove true, it would not mean diverting a penny of research money from research funding to publication costs! It would mean redirecting the very same money that institutions currently spend on subscription charges toward paying instead for publication charges.
(APhS): The nonprofit publishers comprising the DC Principles Coalition are among those who are able to provide public access to literature either immediately or within months of publication without government mandate through corporate and academic subscriptions.This is playing loose with the words "public access." The purpose of an Open Access self-archiving mandate is to provide access to all those would-be users who do not have subscription access, today. Voluntary provision of OA by publishers is of course very welcome, but it is far too few and far between. And the research impact loss problem is now, and urgent.
It would be absurd for the research community to continue sustaining needless annual impact losses in order to wait passively for publisher voluntarism to decide whether and when to remedy them. If publisher voluntarism were indeed inclined to put an end to those impact losses, surely publishers would not be lobbying against the FRPAA self-archiving mandate: they would be supporting it: The distributed author mandate would be saving them the trouble of having to provide OA themselves, from their own resources!
But it is clearly for access-denial, not access-provision, that (some) publishers are lobbying here. Let there be no doubt about that, and that the voluntarism of the DC Principles Coalition is far too little, too late.
(APhS): According to Martin Frank, Ph.D., Executive Director of the American Physiological Society (APS) and a member of the Coalition, "a six-month release mandate may force some journals to shift to a publication model requiring authors to pay for their publications through their Federal grants, diminishing funds available for research to benefit the public good."(1) As noted, this hypothesis -- that mandated self-archiving will cause a conversion to the OA publishing cost-recovery model -- is pure speculation at this time, with no evidence in its support, and the prominent evidence from both the American Physical Society and IOPP contradicting it.Martin Frank, Ph.D.
Executive Director, American Physiological Society
http://www.the-aps.org
(2) But let us suppose, for the sake of argument, that the hypothesis should one day come to pass: does this mean "diminishing funds available for research to benefit the public good"?
(3) What Martin Frank seems to be forgetting in his calculations is that in order to force a shift to the OA publishing cost-recovery model, there first have to be substantial revenue losses for publishers, from institutional subscription cancellations.
(4) But for every single penny of revenue lost by publishers in the form of institutional subscription cancellations, there has to be a penny saved by institutions, in the form of windfall savings.
(5) Hence if publisher revenue losses were ever indeed to force a shift to the OA cost-recovery model, the institutions would have a large annual pot of windfall savings from incoming subscription cancellations upon which to draw, in order to begin paying instead for their own outgoing publication costs.
(6) Hence there would be nothing at all "requiring authors to pay for their publications through their Federal grants, diminishing funds available for research to benefit the public good."
(7) The only thing that would have happened would be the augmentation of the public good derived from research, by maximising its access, usage and impact -- whether or not the hypothetical shift in publish models came to pass.
(8) It is only now -- when there are neither any institutional subscription cancellation pressures, nor any institutional subscription windfall savings -- that it looks as if paying OA publishing costs would require diverting money form research.
(9) Hence it is both self-serving and self-contradictory to float both the "damage" hypothesis and the "research fund diversion" hypothesis in the same breath: If the "damage" is subscription revenue loss, then that is also the diversion: no need to poach research funds!
Issued on September 22, 2006, the letter reads:If this were indeed clearly thought-through and sincerely meant, we could stop right here. Because "the broadest dissemination of scientific literature" is Open Access, and the FRPAA self-archiving mandate will provide Open Access.
Dear Senators Cornyn and Lieberman:
The undersigned senior academic officers write to express our concerns about S.2695, the "Federal Research Public Access Act of 2006."
We agree that the broadest dissemination of scientific literature is good for research.
Letter: However, mandating a six-month public release of journal articles would have negative unintended consequences for the academic community.Are these hypothetical negative unintended consequences negative for the academic community (i.e., researchers and their institutions and users), or for the publishing community? (The two are completely conflated in what follows below.)
Letter: The free posting of unedited author manuscripts by government agencies [1] threatens the integrity of the scientific record, [2] potentially undermines the publisher peer review process, and [3] is not a smart use of funds that could be better used for research.(0) The posting is by authors, not by government agencies: the FRPAA proposal is for the government agencies to mandate that the authors post the manuscripts.
(1) How does posting a free final, peer-reviewed, accepted draft of the author's paper for those would-be users webwide who cannot afford access to the publisher's version of record "threaten the integrity of the scientific record"?
(2) What the FRPAA proposes to require to post is the author's final, peer-reviewed draft, accepted for publication; the only thing it might be missing is some copy-editing: How does that "undermine the publisher peer review process"?
(3) And is it, then, smarter use of funds to subsidise copy-editing with lost research impact?
If copy-editing is such an important added-value, what are publishers worried about? The subscription smart-money will then just keep on paying for it, since that added-value is missing from the author's peer-reviewed final draft, which is merely a supplement for those who cannot afford the publisher's official copy-edited version of record, online or on paper.
(But please let's leave the "peer review process" out of this, because it is not even at issue. The peers review for free, as a service to both authors and publishers; their services are not what the subscription money is being spent on.)
Letter: Scientific publishers, in collaboration with academic institutions, scientists, and libraries, have been at the forefront of innovations that have improved and continue to improve access to research information. As a result, more scientific papers are now available to more people than at any time in history.Absolutely true, and commendable, but irrelevant. Because it is not enough. Substantial amounts of potential research impact are still being needlessly lost, cumulatively, in an online age when this loss can easily be prevented, once and for all, at long last.
The supplementary self-archived author's draft is for all those would-be users whose institutions cannot afford the above-mentioned "innovations and improvements." For without the author's self-archived version, they have no access at all.
For an estimate of how many users are being denied access -- and hence how many authors are being denied impact -- simply look at the studies thay show the degree to which self-archiving enhances article usage and impact.
Letter: Even when federal funds support the research reported in journal articles, these funds do not cover the costs associated with turning raw data into archived scientific manuscripts. The cost of peer review, copy editing, formatting, printing, online publication, search engine development, and permanent archiving ranges from $2,500 - $10,000 per article.Even without challenging those figures, one can point out that all those costs are currently being paid, in full, by subscriptions, with no evidence that self-archiving reduces those subscriptions. If and when self-archiving should ever reduce those subscriptions enough to require another way of meeting those costs, the costs will be met out of the windfall subscription savings.
But for now, this is mere speculation. The only thing that is not speculation is the demonstrated benefits of OA self-archiving to research and researchers, in enhancing research usage and impact.
Nor -- as long as we are speculating -- is it at all clear that if self-archiving were indeed ever to induce subscription cancellations, that "the cost of peer review, copy editing, formatting, printing, online publication, search engine development, and permanent archiving [$2,500 - $10,000 per article]" would all prove irreducible:
It is not only hypothetically possible but quite likely that the cost of implementing peer review [since the peers review for free] could turn out to be the only essential remaining publication cost, and that is only about $500 per article.
The value of copy editing remains to be determined empirically, but formatting, printing, online publication, search engine development, and permanent archiving look very much like the kinds of things that could readily be offloaded onto authors and their institutions, with their distributed network of OA IRs and their distributed and hence much diluted costs per article, nowhere near the current $2,500 - $10,000 figure.
The above is of course all just speculation too, but hypothetical speculation invariably breeds counterspeculation. The only certainty here is that mandated OA self-archiving will be highly beneficial to research usage and impact, as has already been repeatedly demonstrated empirically."The True Cost of the Essentials (Implementing Peer Review)" (Feb 2000)
"Hypothetical Sequel"
Letter: At present, publishers cover these publication costs through the sale of subscriptions. A Federal policy mandating public access after six months would threaten the financial viability of many of these journals through the loss of subscription revenues, forcing them to identify other means to cover costs.First, to repeat: There is no evidence to date that this hypothesis is correct, even in fields that have been self-archiving at 100% for years now.
But should the hypothesis ever prove true, then, yes, it will be necessary to "identify other means to cover costs" (whatever those irreducible costs turn out to be). And the other means of covering those costs is already obvious: Author-institution payment of publishing costs out of institutions' own windfall subscription savings.
Even without cost-cutting and new efficiencies (such as phasing out the paper edition and relying on the worldwide network of OA IRs to provide access, hence leaving only the cost of implementing the peer review service), a forced shift to the OA publishing cost-recovery model after 100% OA had already been reached via mandated self-archiving would merely mean that the money that currently changes hands between institutions and publishers in the form of subscription costs would instead change hands between institutions and publishers in the form of publishing costs.
Note, though, that no matter how shrilly one raises the volume on the hypothesizing and counter-hypothesizing, it is still merely a speculation that mandated self-archiving will force a shift in publishing models. The only objective certainty is that mandated self-archiving will greatly benefit research impact.
Letter: One such means is to shift the costs to the scientists/authors. This is the business model currently used by the Public Library of Science, for example, which recently increased fees to $2,500 per manuscript. These fees either come from [1] the author's Federal research grant -- thereby decreasing the amount available for research -- or [2] from the university, which could ultimately lead to higher institutional costs than those needed for journal subscriptions.PLoS and other OA publishers today are struggling to make ends meet in a world where spontaneous OA self-archiving is still only hovering at 15%, and 100% of institutional journal budgets are still tied up in covering subscription costs. Hence these brave new OA publishers need to find other sources to pay their OA publishing costs.
But on the above hypothetical scenario, a forced shift to OA publishing caused by mandated self-archiving would result from institutional subscription cancellations! Hence the institutions could then use their own windfall savings to pay the irreducible costs in another way: via the OA publishing model. No need to poach from either research funding (1) or other institutional resources (2).
Letter: In fact, some studies have already shown that research intensive universities would have to pay considerably more to gain access to the same amount of research under an author-pays model than a subscription model.This is compounding speculation with speculation, since no one knows what the true costs would turn out to be, under pressure from subscription revenue declining to unsustainable levels because of institutional cancellations.
There is clearly more than enough money in the system already to sustain publication today. Research-intensive universities are also subscription-intensive universities, so one would have to see just what assumptions are being made by studies that claim that these universities would be worse off if there were ever a transition to OA publishing.
The only thing that is sure is that all research institutions would be far better off in terms of their own research impact (and access). The rest is all speculation, assumptions, and guesstimation.
Letter: Mandating free dissemination of scientific manuscripts within six months would significantly limit the ability of non-profit and commercial publishers to cover the upfront reviewing, editing, and production costs of creating these manuscripts. Some journals would simply cease to exist. Others would be much less able to support innovation in scientific publishing and archiving. Ultimately, this could lead to a system in which NIH and other federal agencies must sustain a significant portion of the research publishing enterprise, maintaining 100+ years of archival journals, as well as producing new research articles.Not only is this merely a shriller version of the speculative scenario already mooted above, at a still higher volume, but it throws in a nonsensical and irrelevant alarum about legacy archiving, something that is not even at issue in the FRPAA self-archiving mandate, which only covers prospective author self-archiving, not retrospective journal archiving. (Let the journals hand over their legacy archives, and I'm sure the research and funder community will know what to do about them: don't fret about the cost...)
On the coverage of the prospective costs if/when subscriptions should become unsustainable, the obvious answer remains the same: institutions will cover those costs out of their own subscription savings.
Letter: As a member of the Senate Budget Committee, you are certainly sensitive to the various forces that shape and reshape the Federal budget from year to year. Recently, for example, we learned that the Biomolecular Interaction Network Database -- the world's largest free repository for proteomic data -- lost its funding and curtailed its curation efforts. As leaders in our respective academic institutions, we are profoundly concerned that one unintended consequence of S. 2695 would be to put both our current research publications and our research archives in jeopardy.The FRPAA self-archiving mandate devolves on the distributed network of institutional repositories (IRs) of all the US research institutions. In the unlikely event that someone would ever want to pull the plug on a major central repository such as PubMed Central, the primary research providers, the universities themselves, are certainly likely to become more and more reliant on the IRs, rather than less and less, in our distributed online, networked age. And the costs of creating and maintaining individual OA IRs are so risibly low that it is absurd even to discuss them.
So the obvious and optimal prophylaxis against any risk of central funding loss for central archives is for researchers to do all their self-archiving locally, in their own institution's IR, and let central collections be harvests from those IRs, rather a locus for direct central self-archiving.
Translation: Based on our evidence-free and counter-evidential speculations about risk to publishers, we urge you to renounce the demonstrated benefits to research, researchers, and the tax-paying public that funds them."Central vs. Distributed Archives" (began Jun 1999)(APhS) Given the widespread access to the scientific literature that already exists and the negative unintended consequences this bill will have on the academic community, we urge you to reconsider whether S.2695 is needed.
"PubMed and self-archiving" (began Aug 2003)
"Central versus institutional self-archiving" (began Nov 2003)
"Harold Varmus: 'Self-Archiving is Not Open Access'" (began June 2006)
Thank you for considering our request.As noted above, it would be absurd for the research community to keep sustaining its needless annual impact losses and just sit waiting passively for publisher voluntarism to decide whether and when to remedy them: The voluntarism of the DC Principles Coalition is far too little, too late.
Sincerely yours,
Robert R. Rich, MD, Senior Vice President and Dean, University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicine, Birmingham, AL
Richard P. Saller, Ph.D., Provost, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL
John R. Sladek, Jr., Ph.D., Vice Chancellor, Research, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, CO
Kenneth L. Barker, Ph.D., Provost and Vice President for Research, SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY
Mary J.C. Hendrix, Ph.D., President & Scientific Director, Children's Memorial Research Center, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL
Bruce A. Holm, Ph.D., Senior Vice Provost, SUNY at Buffalo and Executive Director, NYS Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics & Life Sciences, Buffalo, NY
Leonard R. Johnson, Ph.D., Vice Chancellor for Research, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN
Barbara A. Horwitz, Ph.D., Vice Provost-Academic Personnel, University of California, Davis, CA
Richard J. Traystman, Ph.D., Associate Vice President for Research, Planning, and Development, Associate Dean for Basic Science Research, Oregon Health and Sciences University, Portland, OR
David E. Millhorn, Ph.D., Vice President, Office of Research and Economic Development, University of Tennessee System, Knoxville, TNAbout the DC Principles Coalition for Free Access
The DC Principles for Free Access to Science Coalition represents more than 75 of the nation's leading nonprofit medical and scientific societies and publishers. The not-for-profit publishers are committed to working in partnership with scholarly communities such as libraries to ensure that these communities are sustained, science is advanced, research meets the highest standards, and patient care is enhanced with accurate and timely information.
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Friday, September 22. 2006
BOAI Self-Archiving FAQ
 The BOAI Self-Archiving FAQ has now been translated into Russian by Sergey Parinov (many thanks, Seryozha!)
The BOAI Self-Archiving FAQ has now been translated into Russian by Sergey Parinov (many thanks, Seryozha!)Thursday, September 21. 2006
Central versus institutional self-archiving
Let me try to explain why unreflective support for PubMed Central (PMC, and UK PMC) as the locus for direct self-archiving by authors is very unfortunate for Institutional Repositories (IRs), for self-archiving, and for Open Access (OA) progress in general. The reason is very simple, and I very much hope that it will be given some thought by the many who are currently unquestioningly promoting central self-archiving. (Please note that this has nothing to do with the existence and enormous value of PMC itself: only with whether or not PMC (or any other Central Repository [CR]) should be the place where authors self-archive their papers, and the place where institutions and funders mandate that authors should self-archive their papers -- instead of self-archiving them in their own IRs, from which CRs like PMC can then harvest them.)
SUMMARY: NIH's, PLoS's, the Wellcome Trust's and now the UK MRC's unreflective support for PubMed Central (PMC), a Central Repository (CR), as the locus for direct self-archiving by authors is very unfortunate for Institutional Repositories (IRs), for self-archiving, and for Open Access (OA) progress in general. Alma Swan has published key papers on both OA self-archiving policy and institutional versus central self-archiving (IRs vs. CRs) analysing the reasons.
(a) Institutional self-archiving and central self-archiving are at odds in the quest for a universal self-archiving policy solution that will cover all OA research output.
(b) It would be awkward and inefficient to have a different external cross-institution CR as the locus of primary deposit for every funding area, subject area, combination of subject areas, or nation.
(c) Researchers' own IRs are the most natural and efficient way to scale up to covering all of OA space from all disciplines, institutions and nations.
(d) Direct central self-archiving is already obsolete in the OAI era of interoperable OAI-compliant IRs.
(e) The optimal solution is for researchers to self-archive their own papers in their own OAI-compliant IRs and for CRs to be harvested from those distributed IRs.
(f) Universities are in the best position to mandate self-archiving and monitor and reward compliance.
(g) Mandating self-archiving in CRs instead simply creates an unsystematic and incoherent policy that does not scale up to covering all research output from all research institutions.
(h) What the NIH, Wellcome Trust and MRC should be mandating is not direct depositing in PMC, but universal depositing in the fundee's own IR, from which PMC can then harvest collections.
(1) PMC and UK PMC are grounded in two things, (i) the pre-OAI and pre-IR central-archiving model originating from the early and very successful Physics Arxiv and (ii) Harold Varmus's -- and hence NIH's, PLoS's, the Wellcome Trust's and now the UK MRC's fixation on the central (indeed the PMC) model of OA self-archiving. That self-archiving model is already obsolete in the OAI era of distributed, interoperable OAI-compliant IRs.
(2) Although they appear to be complementary -- after all, OAI renders all OAI-compliant archives, whether central or institutional, interoperable, and hence equivalent -- in reality, at this critical point in the evolution of OA self-archiving policy-making, (a) institutional self-archiving and (b) central self-archiving are profoundly at odds with one another in the quest for a systematic, universal self-archiving policy solution that will systematically scale up to cover all research output, from all institutions, in all disciplines, worldwide.
(3) In the OAI-interoperable age, the natural and optimal solution is for researchers to self-archive their own papers in their own OAI-compliant Institutional Repositories (IRs) and for whatever central archives one may wish to have -- whether subject-based or funder-based or national -- to be harvested, via the OAI protocol for metadata harvesting, from the distributed local IRs, rather than deposited, (or re-deposited) directly. That is what the OAI metadata-harvesting protocol was created for!
(4) So although on the surface it looks as if there is room for complementarity, pluralism, and parallelism between Central Repositories (CRs) and Institutional Repositories (IRs), the question of what their optimal interrelationship should be is far more complicated insofar as formulating a systematic, effective OA self-archiving policy is concerned, and ensuring that the policy will scale up to cover all of OA space. There is a profound and important strategic conflict specifically related to institutional and research-funder self-archiving policy (mandates).
(5) Dr. Alma Swan has published key papers on both the subject of OA self-archiving policy and the subject of institutional versus central self-archiving (IRs vs. CRs).
(6) The gist of the strategic and practical conflict between IRs and CRs, as well as the basis for resolving it, is the following:
(7) Universities (and other research institutions) are the primary research providers. It is their researchers who conduct and publish the research. It is they and their researchers who are in a position to provide OA. It is they and their researchers who co-benefit from providing OA by self-archiving their own research output. The natural place for them to self-archive their own research output is in their own respective (OAI-compliant) IRs. This covers all the output of all their disciplines (some research institutions have just one research speciality, whereas others, including all universities, cover most or all research specialties).
(8) Universities (and other research institutions) are real entities, with their own institutional identity, and it is their own institutional visibility and productivity and research impact (along with the impact and progress of research in general) that they are motivated and indeed necessitated to promote and foster. CRs, in contrast, do not correspond to institutional entities with needs of their own. (The partial exception is when a CR is research funder-based, where the funder is an entity with interests. I will return to this.)
(9) Universities (and other research institutions) are also the ones that are in the strongest position to mandate the self-archiving of their own research input, as well as to monitor and to reward compliance with their self-archiving policy. (Again, the only exception is a research funder, or a national government.)
(10) Universities (and other research institutions) are helped in their efforts to mandate OA self-archiving by OA self-archiving mandates from the funders of their research, but (a) not all their research is funded, (b) it would be extremely awkward and inefficient if for a single institutions' authors, there were a different external cross-institution CR that needed to be desposited in for every funder and every subject and every other possible combination of subjects (and nations!) .
(11) Instead, the natural and efficient way to gather content into CRs -- whether funder CRs or subject-based CRs or multidisciplinary CRs or national CRs -- is to selectively harvest their contents from the individual, distributed IRs of the researchers' own institutions.
(12) IRs are also the most natural and efficient and systematic and universal way to scale up to cover all of OA space -- originating from all disciplines, at all institutions, in all nations.
(13) A few generic OAI-compliant CRs are fine for provisionally or even permanently depositing research by researchers whose institutions do not yet have an IR (or by researchers who do not even have an institution!); but apart from that, direct depositing in CRs is extremely counterproductive at a time when self-archiving has not yet been established as a systematic research imperative.
(14) The optimal thing for both research institutions and funders to do now is to mandate self-archiving in the researcher's own IR (except where a default generic CR is needed because the researcher's institution does not yet have an IR).
(15) Compliance can be monitored and rewarded, primarily by the researcher's own institution, but also through the grant-fulfilment conditions of the funder.
(16) This will systematically scale up to cover all disciplines, at all institutions, globally.
(17) If central self-archiving (e.g., in PMC) is mandated instead, that simply creates an unsystematic and incoherent policy that does not translate into a general means of covering all research output of all research institutions.
(18) The NIH, Wellcome Trust and MRC self-archiving policies (though they make important contributions to OA) are hence complicating and retarding progress toward a universal, systematic solution toward making all institutions' research output OA because of their insistence on direct deposit in PMC.
(19) What the NIH, Wellcome Trust and MRC should be mandating is not arbitrary direct depositing in PMC, but universal depositing in the fundee's own IR, from which PMC (and any other CRs) can then harvest collections, if they wish.
(20) In this way, institutional and funder self-archiving mandates can be synergistic instead of antagonistic (confusing researchers about where to self-archive, arousing resentment about the need to do multiple deposits; failing to generalize and scale up to a systematic, universal self-archiving policy and solution, for all institutions, disciplines, funders and nations, and in general retarding instead of accelerating progress in the formulation of effective and compatible self-archiving policies globally).
(21) The last point is that not only is primary depositing in CRs a very bad idea, but in the OAI-age CRs need not "house" the full-texts at all: they really only need to be "virtual archives" in much the way that google or OAIster is: They harvest the metadata and links, allow focussed search, and then point back to the IRs for accessing the full-text itself. The notion of having to have one central "place" in which to put all papers is obsolete in the OAI age. (I am not referring to redundancy and preservation issues, for which some duplication is useful and indeed necessary; I am referring to the fallacious notion that we need CRs in order to have the target content for searching and accessing "all in one place." We do not; and we should not. Yet I am almost certain that this is the main reason so many people think they need a CR!)
Many well-meaning advocates of OA do not yet understand much of this, imagining that CRs like PMC will in some mysterious way manage to cover all of OA space. I hope the summary above will help to redirect the welcome and important contributions of the supporters of the NIH-PLoS-Wellcome-MRC OA initiatives in a direction that is more helpful for scaling up to cover the world's research output as a whole.
Pertinent Prior American Scientist Open Access Forum Topic Threads:
"Central vs. Distributed Archives" (began Jun 1999)Stevan Harnad
"PubMed and self-archiving" (began Aug 2003)
"Central versus institutional self-archiving" (began Nov 2003)
"Harold Varmus: 'Self-Archiving is Not Open Access'" (began June 2006)
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Saturday, September 16. 2006
"Publish or Perish" Illustrated
 Judith Economos has just created a series of cartoons to illustrate "Publish or Perish" (in support of Open Access).
Judith Economos has just created a series of cartoons to illustrate "Publish or Perish" (in support of Open Access).Bilingual (French/English) version « Publier ou périr » : PDF or Powerpoint
English-only version: PDF or Powerpoint
Please feel free to use them to promote Open Access! (Recommended background soundtrack: Beatbox)
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Friday, September 8. 2006
115 US university presidents and provosts endorse FRPAA self-archiving mandate proposal
More and more US university presidents and provosts are signing to support the proposed  FRPAA self-archiving mandate. Let us hope that they will not now sit waiting for the Act to pass, but will also go on to sign a self-archiving mandate for each of their own respective universities -- and then register their policies in ROARMAP for other universities to emulate. (The Immediate-Deposit/Optional-Access [ID/OA] mandate is the optimal policy to adopt -- infinitely preferable to the "Optional Delayed Deposit" mandates that are currently being contemplated instead of giving the details deeper and more careful thought.)
FRPAA self-archiving mandate. Let us hope that they will not now sit waiting for the Act to pass, but will also go on to sign a self-archiving mandate for each of their own respective universities -- and then register their policies in ROARMAP for other universities to emulate. (The Immediate-Deposit/Optional-Access [ID/OA] mandate is the optimal policy to adopt -- infinitely preferable to the "Optional Delayed Deposit" mandates that are currently being contemplated instead of giving the details deeper and more careful thought.)
 (UK vice-chancellors and pro-vice-chancellors should hasten to adopt ID/OA too, now that half the RCUK research councils and the Wellcome Trust have already mandated self-archiving! The European Commission is next...)
(UK vice-chancellors and pro-vice-chancellors should hasten to adopt ID/OA too, now that half the RCUK research councils and the Wellcome Trust have already mandated self-archiving! The European Commission is next...)
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
 FRPAA self-archiving mandate. Let us hope that they will not now sit waiting for the Act to pass, but will also go on to sign a self-archiving mandate for each of their own respective universities -- and then register their policies in ROARMAP for other universities to emulate. (The Immediate-Deposit/Optional-Access [ID/OA] mandate is the optimal policy to adopt -- infinitely preferable to the "Optional Delayed Deposit" mandates that are currently being contemplated instead of giving the details deeper and more careful thought.)
FRPAA self-archiving mandate. Let us hope that they will not now sit waiting for the Act to pass, but will also go on to sign a self-archiving mandate for each of their own respective universities -- and then register their policies in ROARMAP for other universities to emulate. (The Immediate-Deposit/Optional-Access [ID/OA] mandate is the optimal policy to adopt -- infinitely preferable to the "Optional Delayed Deposit" mandates that are currently being contemplated instead of giving the details deeper and more careful thought.) Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Sunday, September 3. 2006
The Geeks and the Irrational
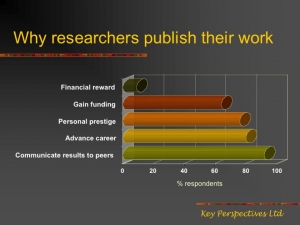 A promise: If it should turn out that the spontaneous author uptake rate for the "hybrid gold open access" option (i.e., journals that give authors a choice between either conventional subscription-based publication or paying to make their own article open access) significantly exceeds the spontaneous author uptake rate for "green open access" self-archiving (currently only about 15%, averaged across all fields, even though 94% of journals have given authors their green light for immediate OA self-archiving), then this weary archivangelist will retire to his tent, in defeat and dismay, at having wasted a decade and a half on trying to maximize the impact of human rationality, only to discover
A promise: If it should turn out that the spontaneous author uptake rate for the "hybrid gold open access" option (i.e., journals that give authors a choice between either conventional subscription-based publication or paying to make their own article open access) significantly exceeds the spontaneous author uptake rate for "green open access" self-archiving (currently only about 15%, averaged across all fields, even though 94% of journals have given authors their green light for immediate OA self-archiving), then this weary archivangelist will retire to his tent, in defeat and dismay, at having wasted a decade and a half on trying to maximize the impact of human rationality, only to discover 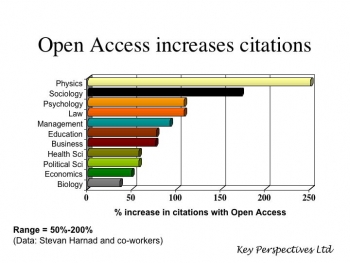 that the sole thing that had been missing all along -- as Thomas Walker had suggested in 1998, in the proposal that launched the American Scientist Open Access Forum -- was the option to purchase the extra visibility at a price!
that the sole thing that had been missing all along -- as Thomas Walker had suggested in 1998, in the proposal that launched the American Scientist Open Access Forum -- was the option to purchase the extra visibility at a price!My own guess, though, is that researchers are no more likely to do, spontaneously, for a fee, what they would not do, spontaneously, for free, for well over a decade now, despite its substantial benefits to themselves and their research.
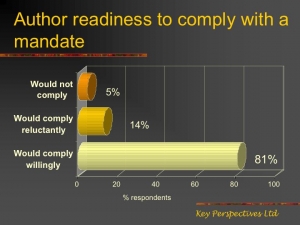
As 95% of researchers sampled predicted, repeatedly, when surveyed by Alma Swan (2006) of Key Perspectives and others; and as researchers confirmed by their actual behaviour when submission rates for IRs with and without self-archiving mandates were compared (Sale 2006): Most researchers will not bother to self-archive until and unless they are required to do so by their institutions and/or funders: Not for free, and even less likely for a fee!
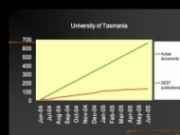
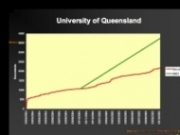
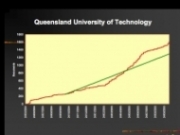
Growth rates for self-archived articles (red) relative to annual article output (green) for three different IRs (with Library Help = +L; with Mandate = +M): (1) -L -M (2) +L -M (3) +L +M
(Data and graphs from A. Sale; all figures accompanying this posting are from Key Perspectives)
Hence it is Immediate-Deposit & Optional-Access Self-Archiving Mandates (ID/OA)
 by researchers' institutions and funders that will propel self-archiving rates from their current spontaneous 15% rut into unstoppable growth toward 100% -- given that Rationality and Rational Self-Interest alone did not prove to be enough to inspire researchers to self-archive, but they did prove to be enough to inspire their institutions and funders to extend their existing "publish-or-perish" mandates to "publish-and-self-archive"; and given that few will choose to pay for what they could have for free but couldn't be bothered to provide till mandated to do so...
by researchers' institutions and funders that will propel self-archiving rates from their current spontaneous 15% rut into unstoppable growth toward 100% -- given that Rationality and Rational Self-Interest alone did not prove to be enough to inspire researchers to self-archive, but they did prove to be enough to inspire their institutions and funders to extend their existing "publish-or-perish" mandates to "publish-and-self-archive"; and given that few will choose to pay for what they could have for free but couldn't be bothered to provide till mandated to do so... (Only IF AND WHEN the urgent question should ever become (1) how to pay publication costs (subscriptions having been cancelled) rather than (2) how to end access-denial and impact-loss (as now), THEN the windfall savings from the subscription cancellations will be the rational source out of which to pay the publication costs. To pay for OA now, in advance, when all the money is all still tied up in subscriptions, when all costs are still being covered, and when catastrophic cancellations are only a hypothetical possibility -- well, you find your own preferred i-word for describing it...)
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
References
Hajjem, C., Harnad, S. and Gingras, Y. (2005) Ten-Year Cross-Disciplinary Comparison of the Growth of Open Access and How it Increases Research Citation Impact. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin 28(4) pp. 39-47.
Sale, Arthur (2006a) Researchers and institutional repositories, in Jacobs, Neil, Eds. Open Access: Key Strategic, Technical and Economic Aspects, chapter 9, pages 87-100. Chandos Publishing (Oxford) Limited.
Swan, A. (2006) The culture of Open Access: researchers' views and responses, in Jacobs, N., Eds. Open Access: Key Strategic, Technical and Economic Aspects, chapter 7. Chandos.
Friday, September 1. 2006
Self-Archive Now: No Need to Negotiate Rights
OhioLINK has made a very welcome recommendation to self-archive.
What is missing from the otherwise useful information that OhioLINK lists, curiously, is a link to the BOAI Self-Archiving FAQ, which has been in place since 2002! And whereas it is always good to negotiate the retention of rights if an author can and wishes, it is erroneous to imply that that is a necessary precondition for self-archiving.
Ninety-four percent of journals already endorse immediate (non-embargoed) OA self-archiving; for articles published in the remaining 6% there is the readily available optionof depositing their full-texts and metadata immediately upon acceptance for publication, but making only their metadata immediately accessible webwide, while provisionally setting access to their full-text as "Closed Access" during any publisher embargo period: Meanwhile almost-immediate, almost-OA for each individual would-be user can still be provided by the author on one-on-one basis, via the semi-automatic EMAIL EPRINT REQUEST button now being added to the principle Institutional Repository (IR) softwares.
Hence it is now possible to self-archive 100% of the final drafts of peer-reviewed journal articles whether or not the author can or wishes to successfully negotiate the retention of rights. Do not wait for successful rights negotiation before self-archiving -- or before mandating self-archiving. Self-archive now, for the sake of research impact and progress (and negotiate after, if you wish).
And on no account feel that you need to switch journals in order to do this!
American Scientist Open Access Forum
What is missing from the otherwise useful information that OhioLINK lists, curiously, is a link to the BOAI Self-Archiving FAQ, which has been in place since 2002! And whereas it is always good to negotiate the retention of rights if an author can and wishes, it is erroneous to imply that that is a necessary precondition for self-archiving.
Ninety-four percent of journals already endorse immediate (non-embargoed) OA self-archiving; for articles published in the remaining 6% there is the readily available optionof depositing their full-texts and metadata immediately upon acceptance for publication, but making only their metadata immediately accessible webwide, while provisionally setting access to their full-text as "Closed Access" during any publisher embargo period: Meanwhile almost-immediate, almost-OA for each individual would-be user can still be provided by the author on one-on-one basis, via the semi-automatic EMAIL EPRINT REQUEST button now being added to the principle Institutional Repository (IR) softwares.
Hence it is now possible to self-archive 100% of the final drafts of peer-reviewed journal articles whether or not the author can or wishes to successfully negotiate the retention of rights. Do not wait for successful rights negotiation before self-archiving -- or before mandating self-archiving. Self-archive now, for the sake of research impact and progress (and negotiate after, if you wish).
And on no account feel that you need to switch journals in order to do this!
Original American Scientist Open Access Forum Thread began:Stevan Harnad
"Self-Archiving the Refereed Journal Literature" (Apr 1999)
American Scientist Open Access Forum
(Page 1 of 1, totaling 8 entries)
EnablingOpenScholarship (EOS)
Quicksearch
Syndicate This Blog
Materials You Are Invited To Use To Promote OA Self-Archiving:
Videos:
audio WOS
Wizards of OA -
audio U Indiana
Scientometrics -
The American Scientist Open Access Forum has been chronicling and often directing the course of progress in providing Open Access to Universities' Peer-Reviewed Research Articles since its inception in the US in 1998 by the American Scientist, published by the Sigma Xi Society.
The American Scientist Open Access Forum has been chronicling and often directing the course of progress in providing Open Access to Universities' Peer-Reviewed Research Articles since its inception in the US in 1998 by the American Scientist, published by the Sigma Xi Society.
The Forum is largely for policy-makers at universities, research institutions and research funding agencies worldwide who are interested in institutional Open Acess Provision policy. (It is not a general discussion group for serials, pricing or publishing issues: it is specifically focussed on institutional Open Acess policy.)
You can sign on to the Forum here.
Archives
Calendar
Categories
Blog Administration
Statistics
Last entry: 2018-09-14 13:27
1129 entries written
238 comments have been made


