Quicksearch
Your search for metrics returned 102 results:
Sunday, February 15. 2009
UK's HEFCE Squandering Its Credibility and Assets In Assessing Research Assessment

Corbyn, Zoë (2009) "Conflict of interest warning over Evidence sale" [to Thompson Reuters]. Times Higher Education Supplement. 22 January 2009There is indeed not only a potential but an actual conflict of interest when the party that is comparing and assessing the different candidate data and databases that can be used in UK national research assessment is the commercial producer of one of the candidate databases.
HEFCE is sleep-walking in letting this happen, and in several other decisions it is making without thinking them through properly, including the failure to test and validate a rich variety of other potential research-assessment metrics, over and above the few that either Thompson-Reuters ISI or its (now disadvantaged) rival SCOPUS can offer, especially the ones provided by the growing worldwide network of Open Access Repositories.
HEFCE is well on the way to foolishly locking itself into dependence on only what is available from a single commercial provider -- under the guise of an objective assessment by an independent honest broker.
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Harnad, S. (2001) Research access, impact and assessment. Times Higher Education Supplement 1487: p. 16.
Brody, T., Kampa, S., Harnad, S., Carr, L. and Hitchcock, S. (2003) Digitometric Services for Open Archives Environments. In Proceedings of European Conference on Digital Libraries, Trondheim, Norway.
Harnad, S., Carr, L., Brody, T. & Oppenheim, C. (2003) Mandated online RAE CVs Linked to University Eprint Archives: Improving the UK Research Assessment Exercise whilst making it cheaper and easier. Ariadne 35.
Harnad, S. (2006) Online, Continuous, Metrics-Based Research Assessment. Technical Report, ECS, University of Southampton.
Carr, L., Hitchcock, S., Oppenheim, C., McDonald, J. W., Champion, T. and Harnad, S. (2006) Extending journal-based research impact assessment to book-based disciplines. Technical Report, ECS, University of Southampton.
Harnad, S. (2007) Open Access Scientometrics and the UK Research Assessment Exercise. In Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics 11(1), pp. 27-33, Madrid, Spain. Torres-Salinas, D. and Moed, H. F., Eds.
Brody, T., Carr, L., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Time to Convert to Metrics. Research Fortnight 17-18.
Brody, T., Carr, L., Gingras, Y., Hajjem, C., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Incentivizing the Open Access Research Web: Publication-Archiving, Data-Archiving and Scientometrics. CTWatch Quarterly 3(3).
Harnad, S. (2008) Self-Archiving, Metrics and Mandates. Science Editor 31(2) 57-59
Harnad, S. (2008) Validating Research Performance Metrics Against Peer Rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8 (11) doi:10.3354/esep00088 (Special issue: The Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Evaluating Scholarly Performance)
Harnad, S., Carr, L. and Gingras, Y. (2008) Maximizing Research Progress Through Open Access Mandates and Metrics. Liinc em Revista 4(2).
Harnad, S. (2009) Multiple metrics required to measure research performance. Nature (Correspondence) 457 (785) (12 February 2009)
Thursday, January 22. 2009
The fundamental importance of capturing cited-reference metadata in Institutional Repository deposits
 On 22-Jan-09, at 5:18 AM, Francis Jayakanth wrote on the eprints-tech list:
On 22-Jan-09, at 5:18 AM, Francis Jayakanth wrote on the eprints-tech list:"Till recently, we used to include references for all the uploads that are happening into our repository. While copying and pasting metadata content from the PDFs, we don't directly paste the copied content onto the submission screen. Instead, we first copy the content onto an editor like notepad or wordpad and then copy the content from an editor on to the submission screen. This is specially true for the references.The items in an article's reference list are among the most important of metadata, second only to the equivalent information about the article itself. Indeed they are the canonical metadata: authors, year, title, journal. If each Institutional Repository (IR) has those canonical metadata for every one of its deposited articles as well as for every article cited by every one of its deposited articles, that creates the glue for distributed reference interlinking and metric analysis of the entire distributed OA corpus webwide, as well as a means of triangulating institutional affiliations and even name disambiguation.
"Our experience has been that when the references are copied and pasted on to an editor like notepad or wordpad from the PDF file, invariably non-ascii characters found in almost every reference. Correcting the non-ascii characters takes considerable amount of time. Also, as to be expected, the references from difference publishers are in different styles, which may not make reference linking straight forward. Both these factors forced us take a decision to do away with uploading of references, henceforth. I'll appreciate if you could share your experiences on the said matter."
Yes, there are some technical problems to be solved in order to capture all references, such as they are, filtering out noise, but those technical problems are well worth solving (and sharing the solution) for the great benefits they will bestow.
The same is true for handling the numerous (but finite) variant formats that references may take: Yes, there are many, including different permutations in the order of the key components, abbreviations, incomplete components etc., but those too are finite, can be solved once and for all to a very good approximation, and the solution can be shared and pooled across the distributed IRs and their softwares. And again, it is eminently worthwhile to make the relatively small effort to do this, because the dividends are so vast.
I hope the IR community in general -- and the EPrints community in particular -- will make the relatively small, distributed, collaborative effort it takes to ensure that this all-important OA glue unites all the IRs in one of their most fundamental functions.
(Roman Chyla has replied to eprints-tech with one potential solution: "The technical solution has been there for quite some time, look at citeseer where all the references are extracted automatically (the code of the citeseer, the old version, was available upon request - I dont know if that is the case now, but it was in the past). That would be the right way to go, imo. I think to remember one citeseer-based library for economics existed, so not only the computer-science texts with predictable reference styles are possible to process. With humanities it is yet another story.")Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Tuesday, January 13. 2009
Validating Multiple Metrics As Substitutes for Expert Evaluation of Research Performance
Harnad, Stevan (2009) Multiple metrics required to measure research performance. Nature (Correspondence) 457 (785) (12 February 2009) doi :10.1038/457785a;
 Nature's editorial "Experts still needed" (Nature 457: 7-8, 1 January 2009) is right that no one metric alone can substitute for the expert evaluation of research performance (based on already-published, peer-reviewed research), because no single metric (including citation counts) is strongly enough correlated with expert judgments to take their place. However, some individual metrics (such as citation counts) are nevertheless significantly correlated with expert judgments; and it is likely that a battery of multiple metrics, used jointly, will be even more strongly correlated with expert judgments. That is the unique opportunity that the current UK Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) -- and our open, online age, with its rich spectrum of potential performance indicators -- jointly provide: the opportunity to systematically cross-validate a rich and diverse battery of candidate metrics of research productivity, performance and impact (including citations, co-citations, downloads, tags, growth/decay metrics, etc.) against expert judgments, field by field. The rich data that the 2008 RAE returns have provided make it possible to do this validation exercise now too, for all disciplines, on a major nation-sized database. If successfully validated, the metric batteries can then not only pinch-hit for experts in future RAEs, but they will provide an open database that allows anyone, anywhere, any time to do comparative evaluations of research performance: continuous assessment and answerability.
Nature's editorial "Experts still needed" (Nature 457: 7-8, 1 January 2009) is right that no one metric alone can substitute for the expert evaluation of research performance (based on already-published, peer-reviewed research), because no single metric (including citation counts) is strongly enough correlated with expert judgments to take their place. However, some individual metrics (such as citation counts) are nevertheless significantly correlated with expert judgments; and it is likely that a battery of multiple metrics, used jointly, will be even more strongly correlated with expert judgments. That is the unique opportunity that the current UK Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) -- and our open, online age, with its rich spectrum of potential performance indicators -- jointly provide: the opportunity to systematically cross-validate a rich and diverse battery of candidate metrics of research productivity, performance and impact (including citations, co-citations, downloads, tags, growth/decay metrics, etc.) against expert judgments, field by field. The rich data that the 2008 RAE returns have provided make it possible to do this validation exercise now too, for all disciplines, on a major nation-sized database. If successfully validated, the metric batteries can then not only pinch-hit for experts in future RAEs, but they will provide an open database that allows anyone, anywhere, any time to do comparative evaluations of research performance: continuous assessment and answerability.(Note that what is at issue is whether metrics can substitute for costly and time-consuming expert rankings in the retrospective assessment of published, peer-reviewed research. It is of course not peer review itself -- another form of expert judgment -- that metrics are being proposed to replace [or simplify and supplement], for either submitted papers or research proposals.)
Harnad, S. (2008) Validating Research Performance Metrics Against Peer Rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8 (11) doi:10.3354/esep00088 Special Issue: The Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Evaluating Scholarly Performance
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Monday, December 1. 2008
What Institutions Can Do To Facilitate the Transition to Open Access

In Ariadne 57, October 2008, Leo Waaijers has written an article on "What Institutions Can Do to Ease Open Access."
SUMMARY: Leo Waaijers recommends (1) that authors should retain copyright, (2) that institutions should use metrics richer than just the journal impact factor to assess their researchers, and (3) and that "supra-institutional organisations" (such as the European University Association) should "take the necessary initiative" for "[s]witching to Open Access" [OA] from the "traditional subscription model."
It is good for authors to retain copyright whenever they can, but it is not necessary -- and hence gratuitously raises the bar -- if stipulated as a precondition for providing or mandating OA: The only thing necessary for providing or mandating OA is that authors should deposit in their Institutional Repositories (IRs) (and that their institutions and funders should mandate that they deposit) the final drafts of their peer-reviewed journal articles, which 63% of journals already formally endorse making OA immediately upon acceptance. (The remaining 37% can be provisionally deposited in Closed Access, likewise immediately upon acceptance, with the IR's semi-automatic "email eprint request" button tiding over all user needs during any publisher embargo, during which the author can also try to negotiate copyright retention with the publisher, if he wishes. But on no account should copyright retention be required as a precondition, either for depositing or for adopting an institutional mandate to deposit.)
It is good to use richer metrics, but these will not generate OA; rather, OA will generate richer metrics.
Institutions can mandate deposit in IRs, and deposits can be made OA, but this is Green OA self-archiving of articles published in "traditional subscription model" journals; it is not Gold OA journal publishing. Institutions and funders cannot mandate that publishers switch to Gold OA publishing, nor should they try to mandate that authors switch to Gold OA journals just for the sake of providing OA, since OA can already be provided by mandating Green OA self-archiving, without constraining authors' choice of journal.
Since Open Access (OA) itself needs no "easing," I assume that what Leo meant was something more like: "What Institutions Can Do to Facilitate a Transition to Open Access."
In his article, Leo made three recommendations, which I discuss in an exchange below:
On 1-Dec-08 Leo Waaijers wrote in SPARC-OAForum:
LW:Leo, you are quite right that in order to induce authors to provide Green OA, their institutions and funders must be induced to mandate that they provide Green OA, as far too few authors will otherwise do the few requisite keystrokes. Authors can be mandated by their institutions and funders to do the keystrokes, but institutions and funders cannot be mandated to mandate (except possibly by their governments and tax-payers) -- so how to persuade them to mandate the keystrokes?
Dear Stevan,
Most authors do not self-archive their publications spontaneously. So they must be mandated. But, apart from a few, the mandators do not mandate the authors. In a world according to you they themselves must be supermandated. And so on. This approach only works if somewhere in the mandating hierarchy there is an enlightened echelon that is able and willing to start the mandating cascade.
The means that I (and others) have been using to persuade institutions and funders to mandate that their authors provide OA have been these:
(1) Benefits of Providing OA: Gather empirical evidence to demonstrate the benefits of OA to the author, institution, and funder, as well as to research progress and to tax-paying society (increased accessibility, downloads, uptake, citations, hence increased research impact, productivity, and progress, increased visibility and showcasing for institutions, richer and more valid research performance evaluation for research assessors, enhanced and more visible metrics of research impact -- and its rewards -- for authors, etc.).
(2) Means of Providing OA: Provide free software for making deposit quick, easy, reliable, functional, and cheap, for authors as well as their institutions. Provide OA metrics to monitor, measure and reward OA and OA-generated research impact.
(3) Evidence that Mandating (and Only Mandating) Works: Gather empirical data to demonstrate that (a) the vast majority of authors (> 80%) say, when surveyed, that they would deposit willingly if it were mandated by their institutions and/or funders, but that they will not deposit if it is not mandated (< 15%) (Alma Swan's surveys); and that (b) most authors (> 80%) actually do what they said in surveys they would do (deposit if it is mandated [> 80%] and not deposit if it is not mandated [< 15%] even if they are given incentives and assistance [< 30%] (Arthur Sale's Studies).
(4) Information about OA: Information and evidence about the means and the benefits of providing OA has to be widely and relentlessly provided, in conferences, publications, emails, discussion lists, and blogs. At the same time, misunderstanding and misinformation have to be unflaggingly corrected (over and over and over!)
There are already 58 institutional and funder Green OA mandates adopted and at least 11 proposed and under consideration. So these efforts are not entirely falling on deaf ears (although I agree that 58 out of perhaps 10,000 research institutions [plus funders] worldwide -- or even the top 4000 -- is still a sign of some hearing impairment! But the signs are that audition is improving...)
LW:But alas it is not agreement that we need, but mandates (and keystrokes)! And now -- not in some indeterminate future.
To create such a cascade one needs water (i.e. arguments) and a steep rocky slope (i.e. good conditions). The pro OA arguments do not seem to be the problem. In all my discussions over the last decade authors, managers and librarians alike agreed that the future should be OA also thanks to you, our driving OA archivangelist.
LW:I am one of the many admirers of your splendid efforts and successes in the Netherlands, with SURF/DARE, "Cream of Science," and much else.
So, it must be the conditions that are lacking. This awareness brought me to the writing of an article about these failing conditions. Only if we are able to create better conditions mandates will emerge and be successful on a broad scale. A fortiori, this will make mandates superfluous.
But I am afraid I don't see how the three recommendations made in the Ariadne article will make mandates emerge (nor how they make mandates superfluous). On the contrary, I see the challenge of making the three recommendations prevail to be far, far greater than the challenge of getting Green OA self-archiving mandates to be adopted. Let me explain:
LW Recommendation 1: Transferring the copyright in a publication has become a relic of the past; nowadays a “licence to publish” is sufficient. The author retains the copyrights. Institutions should make the use of such a licence part of their institutional policy.Persuading authors to retain copyright is a far bigger task than just persuading them to deposit (keystrokes): It makes them worry about what happens if their publisher does not agree to copyright retention, and then their article fails to be published in their journal of choice.
Doing the c. 6-minutes-worth of keystrokes that it takes to deposit an article -- even if authors can't be bothered to do those keystrokes until/unless it is mandated -- is at least a sure thing, and that's the end of it.
In contrast, it is not at all clear how long copyright retention negotiations will take in each case, nor whether they will succeed in each case.
Moreover, just as most authors are not doing the deposit keystrokes spontaneously, but only if mandated, they are not doing the copyright retention negotiations either: Do you really think it would be easier to mandate doing copyright retention than to mandate a few keystrokes?
(Harvard has adopted a kind of a copyright-retention mandate, though it has an opt-out, so it is not clear whether it is quite a mandate -- nor is it clear how well it will succeed, either in terms of compliance or in terms of negotiation [nor whether it is even thinkable for universities with authors that have less clout with their publishers than Harvard's]. But there is a simple way to have the best of both worlds by upgrading the Harvard copyright-retention mandate with opt-out into a deposit mandate without opt-out that is certain to succeed, and generalizable to all universities -- the Harvards as well as the Have-Nots. To instead require successful copyright renegotiation as a precondition for providing OA and for mandating OA, however, would be needlessly and arbitrarily to raise the bar far higher than it need be -- and already is -- for persuading institutions and funders to mandate deposit at all: "Upgrade Harvard's Opt-Out Copyright Retention Mandate: Add a No-Opt-Out Deposit Clause.")
LW Recommendation 2: The classic impact factor for a journal is not a good yardstick for the prestige of an author. Modern digital technology makes it possible to tailor the measurement system to the author. Institutions should, when assessing scientists and scholars, switch to this type of measurement and should also promote its further development.This is certainly true, but how does using these potential new impact metrics generate OA or OA mandates, or make OA mandates superfluous? On the contrary, it is OA (and whatever successfully generates OA) that will generate these new metrics (which will, among other things, in turn serve to increase research impact, as well as making it more readily measurable and rewardable)!
Brody, T., Carr, L., Gingras, Y., Hajjem, C., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Incentivizing the Open Access Research Web: Publication-Archiving, Data-Archiving and Scientometrics. CTWatch Quarterly 3(3).
Harnad, S. (2007) Open Access Scientometrics and the UK Research Assessment Exercise. In Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics 11(1), pp. 27-33, Madrid, Spain. Torres-Salinas, D. and Moed, H. F., Eds. h
Harnad, S. (2008) Validating Research Performance Metrics Against Peer Rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8 (11) doi:10.3354/esep00088 The Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Evaluating Scholarly Performance
Shadbolt, N., Brody, T., Carr, L. and Harnad, S. (2006) The Open Research Web: A Preview of the Optimal and the Inevitable, in Jacobs, N., Eds. Open Access: Key Strategic, Technical and Economic Aspects. Chandos.
LW Recommendation 3: The traditional subscription model for circulating publications is needlessly complex and expensive. Switching to Open Access, however, requires co-ordination that goes beyond the level of individual institutions. Supra-institutional organisations, for example the European University Association, should take the necessary initiative.The European University Association has already taken the initiative to recommend that its 791 member universities in 46 countries should all mandate Green OA self-archiving! Now the individual universities need to be persuaded to follow that recommendation. The European Heads of Research Councils have made the same recommendation to their member research councils. (I am optimistic, because, for example, 6 of the 7 RCUK research funding councils have so far already followed the very first of these recommendations to mandate -- from the UK Parliamentary Select Committee on Science and Technology.) And the 28 universities that have already adopted Green OA self-archiving mandates show that institutional mandates are at last gathering momentum too.
But if it is already considerably harder to mandate author copyright-retention than it is to mandate author self-archiving in their institutional repositories (Green OA), it is surely yet another order of magnitude harder to mandate "Switching to Open Access" from the "traditional subscription model":
If authors are likely to resist having to renegotiate copyright with their journal of choice at the risk of not getting published in their journal of choice, just in order to provide OA, they are even more likely to resist having to publish in a Gold OA journal instead of in their journal of choice, just in order to provide OA -- especially as they need do neither: They need merely self-archive.
And journal publishers are likely to resist anyone trying to dictate their economic model to them. (Moreover, publishers' economic policies are beyond the bounds of what is within the university community's mandate to mandate!)
So mandating Green OA is still the fastest, surest, and simplest way to reach universal OA. Let us hope that the "enlightened echelon" of the institutional hierarchy will now set in motion the long overdue "mandating cascade."
Best wishes,
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Saturday, November 22. 2008
Peer Review Selectivity Determines Quality, Not Open Access vs. Toll Access
 In "Open Access: The question of quality," Richard Poynder writes:
In "Open Access: The question of quality," Richard Poynder writes: "Open Access scientometrics... raise the intriguing possibility that if research becomes widely available on the Web the quality of papers published in OA journals may start to overtake, not lag [behind], the quality of papers published in TA journals... Why? Because if these tools were widely adopted the most important factor would no longer be which journal you managed to get your paper published in, but how other researchers assessed the value of your work — measured by a wide range of different indicators, including for instance when and how they downloaded it, how they cited it, and the different ways in which they used it."All true, but how does it follow from this that OA journals will overtake TA journals? As Richard himself states, publishing in an OA journal ("Gold OA") is not the only way to make one's article OA: One can publish in a TA journal and self-archive ("Green OA"). OA scientometrics apply to all OA articles, Green and Gold; so does the OA citation advantage.
Is Richard perhaps conflating TA journals in general with top-TA journals (which may indeed lose some of their metric edge because OA scientometrics is, as Richard notes, calculated at the article- rather than the journal-level)? The only overtaking I see here is OA overtaking TA, not OA journals overtaking TA journals. (Besides, there are top-OA journals too, as Richard notes, and bottom-rung TA ones as well.)
It should also be pointed out that the top journals differ from the rest of the journals not just in their impact factor (which, as Richard points out, is a blunt instrument, being based on journal averages rather than individual-article citation counts) but in their degree of selectivity (peer revew standards): If I am selecting members for a basketball team, and I only accept the tallest 5%, I am likely to have a taller team than the team that is less selective on height.
Selectivity is correlated with impact factor, but it is also correlated with quality itself. The Seglen "skewness" effect (that about 80% of citations go to the top 20% of articles) is not just a within-journal effect: it is true across all articles across all journals. There is no doubt variation within the top journals, but not only are their articles cited more on average, but they are also better quality on average (because of their greater selectivity). And the within-journal variation around the mean is likely to be tighter in those more selective journals than the less-selective journals.
OA will give richer and more diverse metrics; it will help the cream (quality) to rise to the top (citations) unconstrained by whether the journal happens to be TA or OA. But it is still the rigor and selectivity of peer review that does the quality triage in the quality hierarchy among the c. 25,000 peer reviewed journals, not OA.
(And performance evaluation committees are probably right to place higher weight on more selective journals -- and on journals with established, longstanding track-records.)
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Sunday, October 19. 2008
On Metrics and Metaphysics

'the man who is ready to prove that metaphysics is wholly impossible... is a brother metaphysician with a rival theory.'A critique of metrics and European Reference Index for the Humanities (ERIH) by History of Science, Technology and Medicine journal editors has been posted on the Classicists list. ERIH looks like an attempt to set up a bigger, better alternative to the ISI Journal Impact Factor (JIF), tailored specifically for the Humanities. The protest from the journal editors looks as if it is partly anti-JIF, partly opposed to the ERIH approach and appointees, and partly anti-metrics.
Francis Herbert Bradley (1846-1924) Appearance and Reality
Their vision seems rather narrow. In the Open Access era, metrics are becoming far richer, more diverse, more transparent and more answerable than just the ISI JIF: author/article citations, author/article downloads, book citations, growth/decay metrics, co-citation metrics, hub/authority metrics, endogamy/exogamy metrics, link metrics, tag metrics, comment metrics, semiometrics (text-mining) and much more. The days of the univariate JIF are already over. This is not the time to reject metrics; it is the time to test and validate, jointly, as full a battery of candidate metrics as possible, but validating the battery separately for each discipline, against peer ranking or other validated or face-valid standards (as in the UK's RAE 2008).
Brody, T., Kampa, S., Harnad, S., Carr, L. and Hitchcock, S. (2003) Digitometric Services for Open Archives Environments. In Proceedings of European Conference on Digital Libraries 2003, pp. 207-220, Trondheim, Norway.
Brody, T., Carr, L., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Time to Convert to Metrics. Research Fortnight pp. 17-18.
Brody, T., Carr, L., Gingras, Y., Hajjem, C., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Incentivizing the Open Access Research Web: Publication-Archiving, Data-Archiving and Scientometrics. CTWatch Quarterly 3(3).
Carr, L., Hitchcock, S., Oppenheim, C., McDonald, J. W., Champion, T. and Harnad, S. (2006) Extending journal-based research impact assessment to book-based disciplines. Technical Report, ECS, University of Southampton.
Harnad, S. (2001) Research access, impact and assessment. Times Higher Education Supplement 1487: p. 16.
Harnad, S., Carr, L., Brody, T. & Oppenheim, C. (2003) Mandated online RAE CVs Linked to University Eprint Archives: Improving the UK Research Assessment Exercise whilst making it cheaper and easier. Ariadne 35.
Harnad, S. (2006) Online, Continuous, Metrics-Based Research Assessment. Technical Report, ECS, University of Southampton.
Harnad, S. (2007) Open Access Scientometrics and the UK Research Assessment Exercise. In Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics 11(1), pp. 27-33, Madrid, Spain. Torres-Salinas, D. and Moed, H. F., Eds.
Harnad, S. (2008) Self-Archiving, Metrics and Mandates. Science Editor 31(2) 57-59
Harnad, S. (2008) Validating Research Performance Metrics Against Peer Rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8 (11) doi:10.3354/esep00088 The Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Evaluating Scholarly Performance
Harnad, S., Carr, L. and Gingras, Y. (2008) Maximizing Research Progress Through Open Access Mandates and Metrics. Liinc em Revista.
Date: Sun, 19 Oct 2008 11:56:22 +0100
Sender: Classicists
From: Nick Lowe
Subject: History of Science pulls out of ERIH
[As editorial boards and subject associations in other humanities subjects contemplate their options, this announcement by journals in History of Science seems worth passing on in full. Thanks to Stephen Clark for the forward.]Journals under Threat: A Joint Response from History of Science, Technology and Medicine Editors
We live in an age of metrics. All around us, things are being standardized, quantified, measured. Scholars concerned with the work of science and technology must regard this as a fascinating and crucial practical, cultural and intellectual phenomenon. Analysis of the roots and meaning of metrics and metrology has been a preoccupation of much of the best work in our field for the past quarter century at least. As practitioners of the interconnected disciplines that make up the field of science studies we understand how significant, contingent and uncertain can be the process of rendering nature and society in grades, classes and numbers. We now confront a situation in which our own research work is being subjected to putatively precise accountancy by arbitrary and unaccountable agencies.
Some may already be aware of the proposed European Reference Index for the Humanities (ERIH), an initiative originating with the European Science Foundation. The ERIH is an attempt to grade journals in the humanities - including "history and philosophy of science". The initiative proposes a league table of academic journals, with premier, second and third divisions. According to the European Science Foundation, ERIH "aims initially to identify, and gain more visibility for, top-quality European Humanities research published in academic journals in, potentially, all European languages". It is hoped "that ERIH will form the backbone of a fully-fledged research information system for the Humanities". What is meant, however, is that ERIH will provide funding bodies and other agencies in Europe and elsewhere with an allegedly exact measure of research quality. In short, if research is published in a premier league journal it will be recognized as first rate; if it appears somewhere in the lower divisions, it will be rated (and not funded) accordingly.
This initiative is entirely defective in conception and execution. Consider the major issues of accountability and transparency. The process of producing the graded list of journals in science studies was overseen by a committee of four (the membership is currently listed at
No indication has been given of the means through which the list was compiled; nor how it might be maintained in the future. The ERIH depends on a fundamental misunderstanding of conduct and publication of research in our field, and in the humanities in general. Journals' quality cannot be separated from their contents and their review processes. Great research may be published anywhere and in any language. Truly ground-breaking work may be more likely to appear from marginal, dissident or unexpected sources, rather than from a well-established and entrenched mainstream. Our journals are various, heterogeneous and distinct. Some are aimed at a broad, general and international readership, others are more specialized in their content and implied audience. Their scope and readership say nothing about the quality of their intellectual content. The ERIH, on the other hand, confuses internationality with quality in a way that is particularly prejudicial to specialist and non-English language journals.
In a recent report, the British Academy, with judicious understatement, concludes that "the European Reference Index for the Humanities as presently conceived does not represent a reliable way in which metrics of peer-reviewed publications can be constructed" (Peer Review: the Challenges for the Humanities and Social Sciences, September 2007:
Hanne Andersen (Centaurus)
Roger Ariew & Moti Feingold (Perspectives on Science)
A. K. Bag (Indian Journal of History of Science)
June Barrow-Green & Benno van Dalen (Historia mathematica)
Keith Benson (History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences)
Marco Beretta (Nuncius)
Michel Blay (Revue d'Histoire des Sciences)
Cornelius Borck (Berichte zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte)
Geof Bowker and Susan Leigh Star (Science, Technology and Human Values)
Massimo Bucciantini & Michele Camerota (Galilaeana: Journal of Galilean Studies)
Jed Buchwald and Jeremy Gray (Archive for History of Exact Sciences)
Vincenzo Cappelletti & Guido Cimino (Physis)
Roger Cline (International Journal for the History of Engineering & Technology)
Stephen Clucas & Stephen Gaukroger (Intellectual History Review)
Hal Cook & Anne Hardy (Medical History)
Leo Corry, Alexandre Métraux & Jürgen Renn (Science in Context)
D. Diecks & J. Uffink (Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics)
Brian Dolan & Bill Luckin (Social History of Medicine)
Hilmar Duerbeck & Wayne Orchiston (Journal of Astronomical History & Heritage)
Moritz Epple, Mikael Hård, Hans-Jörg Rheinberger & Volker Roelcke (NTM: Zeitschrift für Geschichte der Wissenschaften, Technik und Medizin)
Steven French (Metascience)
Willem Hackmann (Bulletin of the Scientific Instrument Society)
Bosse Holmqvist (Lychnos) Paul Farber (Journal of the History of Biology)
Mary Fissell & Randall Packard (Bulletin of the History of Medicine)
Robert Fox (Notes & Records of the Royal Society)
Jim Good (History of the Human Sciences)
Michael Hoskin (Journal for the History of Astronomy)
Ian Inkster (History of Technology)
Marina Frasca Spada (Studies in History and Philosophy of Science)
Nick Jardine (Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences)
Trevor Levere (Annals of Science)
Bernard Lightman (Isis)
Christoph Lüthy (Early Science and Medicine)
Michael Lynch (Social Studies of Science)
Stephen McCluskey & Clive Ruggles (Archaeostronomy: the Journal of Astronomy in Culture)
Peter Morris (Ambix)
E. Charles Nelson (Archives of Natural History)
Ian Nicholson (Journal of the History of the Behavioural Sciences)
Iwan Rhys Morus (History of Science)
John Rigden & Roger H Stuewer (Physics in Perspective)
Simon Schaffer (British Journal for the History of Science)
Paul Unschuld (Sudhoffs Archiv)
Peter Weingart (Minerva)
Stefan Zamecki (Kwartalnik Historii Nauki i Techniki)
Viviane Quirke, RCUK Academic Fellow in twentieth-century Biomedicine, Secretary of the BSHS, Centre for Health, Medicine and Society, Oxford Brookes University
Friday, October 10. 2008
Open Access Book-Impact and "Demotic" Metrics

SUMMARY: Unlike with OA's primary target, journal articles, the deposit of the full-texts of books in Open Access Repositories cannot be mandated, only encouraged. However, the deposit of book metadata + plus + reference-lists can and should be mandated. That will create the metric that the book-based disciplines need most: a book citation index. ISI's Web of Science only covers citations of books by (indexed) journal articles, but book-based disciplines' biggest need is book-to-book citations. Citebase could provide that, once the book reference metadata are being deposited in the IRs too, rather than just article postprints. (Google Books and Google Scholar are already providing a first approximation to book citation count.) Analogues of "download" metrics for books are also potentially obtainable from book vendors, beginning with Amazon Sales Rank. In the Humanities it also matters for credit and impact how much the non-academic (hence non-citing) public is reading their books ("Demotic Metrics"). IRs can not only (1) add book-metadata/reference deposit to their OA Deposit Mandates, but they can (2) harvest Amazon book-sales metrics for their book metadata deposits, to add to their IR stats. IRs can also already harvest Google Books (and Google Scholar) book-citation counts today, as a first step toward constructing a distributed, universal OA book-citation index. The Dublin humanities metrics conference was also concerned about other kinds of online works, and how to measure and credit their impact: Metrics don't stop with citation counts and download counts. Among the many "Demotic metrics" that can also be counted are link-counts, tag-counts, blog-mentions, and web mentions. This applies to books/authors, as well as to data, to courseware and to other identifiable online resources. We should hasten the progress of book metrics, and that will in turn accelerate the growth in OA's primary target content: journal articles, as well as increasing support for institutional and funder OA Deposit Mandates.
The deposit of the full-texts of book-chapters and monographs in Open Access Repositories should of course be encouraged wherever possible, but, unlike with journal articles, full-text book deposit itself cannot be mandated.
The most important additional thing that the OA movement should be singling out and emphasizing -- over and above the Immediate Deposit (IR) Mandate plus the email-eprint-request Button and the use of metrics to motivate mandates -- is the author deposit of all book metadata+plus+reference+lists in the author's OA Institutional Repository (IR). That will create the metric that the book-based disciplines need the most.
This has been mentioned before, as a possibility and a desideratum for institutional (and funder) OA policy, but it is now crystal clear why it is so important (and so easy to implement).
By systematically ensuring the IR deposit of each book's bibliographic metadata plus its cited-works bibliography, institutions (and funders) are actually creating a book citation index.
This became apparent (again) at the Dublin humanities metrics conference, when ISI's VP Jim Pringle repeated ISI 's (rather weak) response to the Humanities' need for a book citation index, pointing out that "ISI does cover citations of books -- by journal articles."
But that of course is anything but sufficient for book-based disciplines, whose concern is mainly about book-to-book citations!
Yet that is precisely what can be harvested out of IRs (by, for example, Citebase, or a Citebase-like scientometric engine) -- if only the book reference metadata, too, are deposited in the IRs, rather than only article postprints. That immediately begins making the IR network into a unique and much-needed book-citation (distributed) database. (Moreover, Google Books and Google Scholar are already providing a first approximation to this.)
And there's more: Obviously OA IRs will not be able to get book download counts -- analogous to article download counts -- when the only thing deposited is the book's metadata and reference list. However, in his paper at this Dublin conference, Janus Linmans -- in cleaving to his age-old bibliometric measure of library book-holdings lists as the surrogate for book citation counts in his analyses -- inadvertently gave me another obvious idea, over and above the deposit and harvesting of book reference metadata:
Library holdings are just one, weak, indirect metric of book usage (and Google Book Collections already collects some of those data). But far better analogues of "downloads" for books are potentially obtainable from book vendors, beginning with Amazon Sales Rank, but eventually including conventional book vendors too (metrics do not end with web-based data):
The researchers from the Humanities stressed in Dublin that the book-to-book (and journal-to-book and book-to-journal) citation counts would be most welcome and useful, but in the Humanities even those do not tell the whole story, because it also matters for the credit and impact of a Humanities' researcher how much the non-academic (hence non-citing) public is reading their books too. (Let us call these non-academic metrics "Demotic Metrics.")
Well, starting with a systematic Amazon book-sales count, per book deposited in the IR (and eventually extended to many book-vendors, online and conventional), the ball can be set in motion very easily. IRs can not only formally (1) add book-metadata/reference deposit to their OA Deposit Mandates, but they can (2) systematically harvest Amazon book-sales metrics for their book items to add to their IR stats for each deposit.
And there's more: IRs can also harvest Google Books (and Google Scholar) book-citation counts, already today, as a first approximation to constructing a distributed, universal OA book-citation index, even before the practice of depositing book metadata/reference has progressed far enough to provide useful data on its own: Whenever book metadata are deposited in an IR, the IR automatically does (i) an Amazon query (number of sales of this book) plus (ii) a Google-Books/Google-Scholar query (number of citations of this book).
These obvious and immediately feasible additions to an institutional OA mandate and to its IR software configuration and functionality would not only yield immediate useful and desirable metrics and motivate Humanists to become even more supportive of OA and metrics, but it would help set in motion practices that (yet again) are so obviously optimal and feasible for science and scholarship as to be inevitable.
We should hasten the progress of book metrics, and that will in turn accelerate the growth in OA's primary target content: journal articles, as well as increasing support for institutional and funder OA Deposit Mandates.
One further spin-off of the Dublin Metrics Conference was other kinds of online works, and how to measure and credit their impact: Metrics don't stop with citation counts and download counts! Among the many "Demotic metrics" that can also be counted are link-counts, tag-counts, blog-mentions, and web mentions. This applies to books/authors, as well as to data, to courseware and to other identifiable online resources.
In "Appearance and Reality," Bradley (1897/2002) wrote (of Ayer) that 'the man who is ready to prove that metaphysics is wholly impossible ... is a brother metaphysician with a rival theory.
Well, one might say the same of those who are skeptical about metrics: There are only two ways to measure the quality, importance or impact of a piece of work: Subjectively, by asking experts for their judgment (peer review: and then you have a polling metric!) or objectively, by counting objective data of various kinds. But of course counting and then declaring those counts "metrics" for some criterion or other, by fiat, is not enough. Those candidate metrics have to be validated against that criterion, either by showing that they correlate highly with the criterion, or that they correlate highly with an already validated correlate of the criterion. One natural criterion is expert judgment itself: peer review. Objective metrics can then be validated against peer review. Book citation metrics need to be added to the rich and growing battery of candidate metrics, and so do "demotic metrics."
Brody, T., Kampa, S., Harnad, S., Carr, L. and Hitchcock, S. (2003) Digitometric Services for Open Archives Environments. In Proceedings of European Conference on Digital Libraries 2003, pp. 207-220, Trondheim, Norway.
Brody, T., Carr, L., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Time to Convert to Metrics. Research Fortnight pp. 17-18.
Brody, T., Carr, L., Gingras, Y., Hajjem, C., Harnad, S. and Swan, A. (2007) Incentivizing the Open Access Research Web: Publication-Archiving, Data-Archiving and Scientometrics. CTWatch Quarterly 3(3).
Carr, L., Hitchcock, S., Oppenheim, C., McDonald, J. W., Champion, T. and Harnad, S. (2006) Extending journal-based research impact assessment to book-based disciplines. Technical Report, ECS, University of Southampton.
Harnad, S. (2001) Research access, impact and assessment. Times Higher Education Supplement 1487: p. 16.
Harnad, S., Carr, L., Brody, T. & Oppenheim, C. (2003) Mandated online RAE CVs Linked to University Eprint Archives: Improving the UK Research Assessment Exercise whilst making it cheaper and easier. Ariadne 35.
Harnad, S. (2006) Online, Continuous, Metrics-Based Research Assessment. Technical Report, ECS, University of Southampton.
Harnad, S. (2007) Open Access Scientometrics and the UK Research Assessment Exercise. In Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics 11(1), pp. 27-33, Madrid, Spain. Torres-Salinas, D. and Moed, H. F., Eds.
Harnad, S. (2008) Self-Archiving, Metrics and Mandates. Science Editor 31(2) 57-59
Harnad, S. (2008) Validating Research Performance Metrics Against Peer Rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8 (11) doi:10.3354/esep00088 The Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Evaluating Scholarly Performance
Harnad, S., Carr, L. and Gingras, Y. (2008) Maximizing Research Progress Through Open Access Mandates and Metrics. Liinc em Revista.
Tuesday, September 9. 2008
Research Evaluation, Metrics and Open Access in the Humanities: Dublin 18-20 September

-- Aimed at Arts and Humanities researchers, Deans of Research, Librarians, research group leaders and policy makers within the Coimbra-Group member universities and the Irish University sector...Research Evaluation, Metrics and Open Access in the Humanities
Coimbra-Group Workshop
Trinity College Dublin
18-20 September 2008
-- To compare established and innovative methods and models of research evaluation and assess their appropriateness for the Arts and Humanities sector...
-- To assess the increasing impact of bibliometrical approaches and Open Access policies on the Arts and Humanities sector...
Monday, August 25. 2008
Confirmation Bias and the Open Access Advantage: Some Methodological Suggestions for Davis's Citation Study
Update Jan 1, 2010: See Gargouri, Y; C Hajjem, V Larivière, Y Gingras, L Carr,T Brody & S Harnad (2010) “Open Access, Whether Self-Selected or Mandated, Increases Citation Impact, Especially for Higher Quality Research”
Update Feb 8, 2010: See also "Open Access: Self-Selected, Mandated & Random; Answers & Questions"
SUMMARY: Davis (2008) analyzes citations from 2004-2007 in 11 biomedical journals. For 1,600 of the 11,000 articles (15%), their authors paid the publisher to make them Open Access (OA). The outcome, confirming previous studies (on both paid and unpaid OA), is a significant OA citation Advantage, but a small one (21%, 4% of it correlated with other article variables such as number of authors, references and pages). The author infers that the size of the OA advantage in this biomedical sample has been shrinking annually from 2004-2007, but the data suggest the opposite. In order to draw valid conclusions from these data, the following five further analyses are necessary:
(1) The current analysis is based only on author-choice (paid) OA. Free OA self-archiving needs to be taken into account too, for the same journals and years, rather than being counted as non-OA, as in the current analysis.Davis proposes that an author self-selection bias for providing OA to higher-quality articles (the Quality Bias, QB) is the primary cause of the observed OA Advantage, but this study does not test or show anything at all about the causal role of QB (or of any of the other potential causal factors, such as Accessibility Advantage, AA, Competitive Advantage, CA, Download Advantage, DA, Early Advantage, EA, and Quality Advantage, QA). The author also suggests that paid OA is not worth the cost, per extra citation. This is probably true, but with OA self-archiving, both the OA and the extra citations are free.
(2) The proportion of OA articles per journal per year needs to be reported and taken into account.
(3) Estimates of journal and article quality and citability in the form of the Journal Impact Factor and the relation between the size of the OA Advantage and journal as well as article “citation-bracket” need to be taken into account.
(4) The sample-size for the highest-impact, largest-sample journal analyzed, PNAS, is restricted and is excluded from some of the analyses. An analysis of the full PNAS dataset is needed, for the entire 2004-2007 period.
(5) The analysis of the interaction between OA and time, 2004-2007, is based on retrospective data from a June 2008 total cumulative citation count. The analysis needs to be redone taking into account the dates of both the cited articles and the citing articles, otherwise article-age effects and any other real-time effects from 2004-2008 are confounded.
The Davis (2008) preprint is an analysis of the citations from years c. 2004-2007 in 11 biomedical journals: c. 11,000 articles, of which c. 1,600 (15%) were made Open Access (OA) through “Author Choice” (AC-OA): author chooses to pay publisher for OA). Author self-archiving (SA-OA) articles from the same journals was not measured.Comments on: Davis, P.M. (2008) Author-choice open access publishing in the biological and medical literature: a citation analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology (JASIST) (in press) http://arxiv.org/pdf/0808.2428v1
The result was a significant OA citation advantage (21%) over time, of which 4% was correlated with variables other than OA and time (number of authors, pages, references; whether article is a Review and has a US co-author).
This outcome confirms the findings of numerous previous studies (some of them based on far larger samples of fields, journals, articles and time-intervals) of an OA citation advantage (ranging from 25%-250%) in all fields, across a 10-year range (Hitchcock 2008).
The preprint also states that the size of the OA advantage in this biomedical sample diminishes annually from 2004-2007. But the data seem to show the opposite: that as an article gets older, and its cumulative citations grow, its absolute and relative OA advantage grow too.
The preprint concludes, based on its estimate of the size of the OA citation Advantage, that AC-OA is not worth the cost, per extra citation. This is probably true -- but with SA-OA the OA and the extra citations can be had at no cost at all.
The paper is accepted for publication in JASIST. It is not clear whether the linked text is the unrefereed preprint, or the refereed, revised postprint. On the assumption that it is the unrefereed preprint, what follows is an extended peer commentary with recommendations on what should be done in revising it for publication.
(It is very possible, however, that some or all of these revisions were also recommended by the JASIST referees and that some of the changes have already been made in the published version.)
As it stands currently, this study (i) confirms a significant OA citation Advantage, (ii) shows that it grows cumulatively with article age and (iii) shows that it is correlated with several other variables that are correlated with citation counts.
Although the author argues that an author self-selection bias for preferentially providing OA to higher-quality articles (the Quality Bias, QB) is the primary causal factor underlying the observed OA Advantage, in fact this study does not test or show anything at all about the causal role of QB (or of any of the other potential causal factors underlying the OA Advantage, such as Accessibility Advantage, AA, Competitive Advantage, CA, Download Advantage, DA, Early Advantage, EA, and Quality Advantage, QA; Hajjem & Harnad 2007b).
The following 5 further analyses of the data are necessary. The size and pattern of the observed results, as well as their interpretations, could all be significantly altered (as well as deepened) by their outcome:
(1) The current analysis is based only on author-choice (paid) OA. Free author self-archiving OA needs to be taken into account too, for the same journals and years, rather than being counted as non-OA, as in the current analysis.Commentary on the text of the preprint:
(2) The proportion of OA articles per journal per year needs to be reported and taken into account.
(3) Estimates of journal and article quality and citability in the form of the Journal Impact Factor (journal’s average citations) and the relation between the size of the OA Advantage and journal and article “citation-bracket” need to be taken into account.
(4) The sample-size for the highest-impact, largest-sample journal, PNAS, is restricted and is excluded from some of the analyses. A full analysis of the full PNAS dataset is needed, for the entire 2004-2007 period.
(5) The analysis of the interaction between OA and time, 2004-2007, is based on retrospective data from a June 2008 total cumulative citation count. The analysis needs to be redone taking into account the dates of both the cited articles and the citing articles, otherwise article-age effects and any other real-time effects from 2004-2008 are confounded.
“ABSTRACT… there is strong evidence to suggest that the open access advantage is declining by about 7% per year, from 32% in 2004 to 11% in 2007”It is not clearly explained how these figures and their interpretation are derived, nor is it reported how many OA articles there were in each of these years. The figures appear to be based on a statistical interaction between OA and article-age in a multiple regression analysis for 9 of the 11 journals in the sample. (a) The data from PNAS, the largest and highest-impact journal, are excluded from this analysis. (b) The many variables included in the (full) multiple regression equation (across journals) omit one of the most obvious ones: journal impact factor. (c) OA articles that are self-archived rather than paid author-choice are not identified and included as OA, hence their citations are counted as being non-OA. (d) The OA/age interaction is not based on yearly citations after a fixed interval for each year, but on cumulative retrospective citations in June 2008.
The natural interpretation of Figure 1 accordingly seems to be the exact opposite of the one the author makes: Not that the size of the OA Advantage shrinks from 2004-2007, but that the size of the OA Advantage grows from 2007-2004 (as articles get older and their citations grow). Not only do cumulative citations grow for both OA and non-OA articles from year 2007 articles to year 2004 articles, but the cumulative OA advantage increases (by about 7% per year, even on the basis of this study’s rather slim and selective data and analyses).
This is quite natural, as not only do citations grow with time, but the OA Advantage -- barely detectable in the first year, being then based on the smallest sample and the fewest citations -- emerges with time.
“See Craig et al. [2007] for a critical review of the literature [on the OA citation advantage]”Craig et al’s rather slanted 2007 review is the only reference to previous findings on the OA Advantage cited by the Davis preprint (Harnad 2007a). Craig et al. had attempted to reinterpret the many times replicated positive finding of an OA citation advantage, on the basis of 4 negative findings (Davis & Fromerth, 2007; Kurtz et al., 2005; Kurtz & Henneken, 2007; Moed, 2007), in maths, astronomy and condensed matter physics, respectively. Apart from Davis’s own prior study, these studies were based mainly on preprints that were made OA well before publication. The observed OA advantage consisted mostly of an Early Access Advantage for the OA prepublication preprint, plus an inferred Quality Bias (QB) on the part of authors towards preferentially providing OA to higher quality preprints (Harnad 2007b).
The Davis preprint does not cite any of the considerably larger number of studies that have reported large and consistent OA advantages for postprints, based on many more fields, some of them based on far larger samples and longer time intervals (Hitchcock 2008). Instead, Davis focuses rather single-mindedly on the hypothesis that most or all of the OA Advantage is the result for the self-selection bias (QB) toward preferentially making higher-quality (hence more citeable) articles OA:
“authors selectively choose which articles to promote freely… [and] highly cited authors disproportionately choose open access venues”It is undoubtedly true that better authors are more likely to make their articles OA, and that authors in general are more likely to make their better articles OA. This Quality or “Self-Selection” Bias (QB) is one of the probable causes of the OA Advantage.
However, no study has shown that QB is the only cause of the OA Advantage, nor even that it is the biggest cause. Three of the studies cited (Kurtz et al., 2005; Kurtz & Henneken, 2007; Moed, 2007) showed that another causal factor is Early Access (EA: providing OA earlier results in more citations).
There are several other candidate causal factors in the OA Advantage, besides QB and EA (Hajjem & Harnad 2007b):
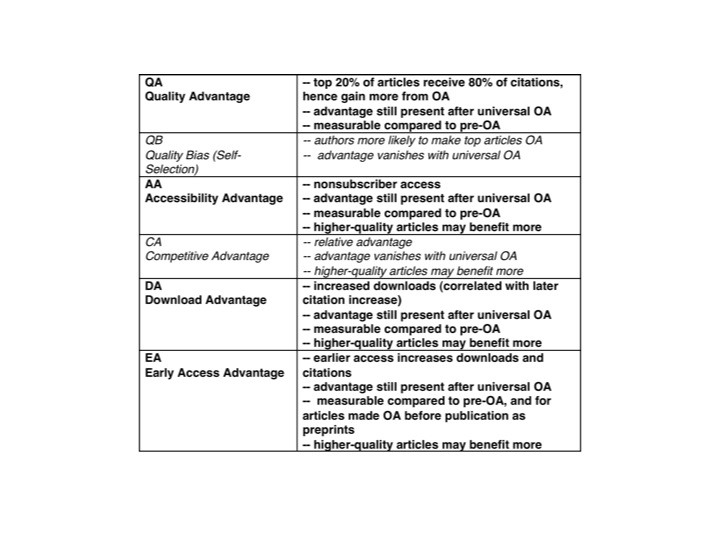 There is the Download (or Usage) Advantage (DA): OA articles are downloaded significantly more, and this early DA has also been shown to be predictive of a later citation advantage in Physics (Brody et al. 2006).
There is the Download (or Usage) Advantage (DA): OA articles are downloaded significantly more, and this early DA has also been shown to be predictive of a later citation advantage in Physics (Brody et al. 2006).There is a Competitive Advantage (CA): OA articles are in competition with non-OA articles, and to the extent that OA articles are relatively more accessible than non-OA articles, they can be used and cited more. Both QB and CA, however, are temporary components of the OA advantage that will necessarily shrink to zero and disappear once all research is OA. EA and DA, in contrast, will continue to contribute to the OA advantage even after universal OA is reached, when all postprints are being made OA immediately upon publication, compared to pre-OA days (as Kurtz has shown for Astronomy, which has already reached universal post-publication OA).
There is an Accessibility Advantage (AA) for those users whose institutions do not have subscription access to the journal in which the article appeared. AA too (unlike CA) persists even after universal OA is reached: all articles then have AA's full benefit.
And there is at least one more important causal component in the OA Advantage, apart from AA, CA, DA and QB, and that is a Quality Advantage (QA), which has often been erroneously conflated with QB (Quality Bias):
Ever since Lawrence’s original study in 2001, the OA Advantage can be estmated in two different ways: (1) by comparing the average citations for OA and non-OA articles (log citation ratios within the same journal and year, or regression analyses like Davis’s) and (2) by comparing the proportion of OA articles in different “citation brackets” (0, 1, 2, 3-4, 5-8, 9-16, 17+ citations).
In method (2), the OA Advantage is observed in the form of an increase in the proportion of OA articles in the higher citation brackets. But this correlation can be explained in two ways. One is QB, which is that authors are more likely to make higher-quality articles OA. But it is also at least as plausible that higher-quality articles benefit more from OA! It is already known that the top c. 10-20% of articles receive c. 80-90% of all citations (Seglen’s 1992 “skewness of science”). It stands to reason, then, that when all articles are made OA, it is the top 20% of articles that are most likely to be cited more: Not all OA articles benefit from OA equally, because not all articles are of equally citable quality.
Hence both QB and QA are likely to be causal components in the OA Advantage, and the only way to tease them apart and estimate their individual contributions is to control for the QB effect by imposing the OA instead of allowing it to be determined by self-selection. We (Gargouri, Hajjem, Gingras, Carr & Harnad, in prep.) are completing such a study now, comparing mandated and unmandated OA; and Davis et al 2008 have just published another study on randomized OA for 11 journals:
“In the first controlled trial of open access publishing where articles were randomly assigned to either open access or subscription-access status, we recently reported that no citation advantage could be attributed to access status (Davis, Lewenstein, Simon, Booth, & Connolly, 2008)”This randomized OA study by Davis et al. was very welcome and timely, but it had originally been announced to cover a 4-year period, from 2007-2010, whereas it was instead prematurely published in 2008, after only one year. No OA advantage at all was observed in that 1-year interval, and this too agrees with the many existing studies on the OA Advantage, some based on far larger samples of journals, articles and fields: Most of those studies (none of them randomized) likewise detected no OA citation advantage at all in the first year: It is simply too early. In most fields, citations take longer than a year to be made, published, ISI-indexed and measured, and to make any further differentials (such as the OA Advantage) measurable. (This is evident in Davis’s present preprint too, where the OA advantage is barely visible in the first year (2007).)
The only way the absence of a significant OA advantage in a sample with randomized OA can be used to demonstrate that the OA Advantage is only or mostly just a self-selection bias (QB) is by also demonstrating the presence of a significant OA advantage in the same (or comparable) sample with nonrandomized (i.e., self-selected) OA.
But Davis et al. did not do this control comparison (Harnad 2008b). Finding no OA Advantage with randomized OA after one year merely confirms the (widely observed) finding that one year is usually too early to detect any OA Advantage; but it shows nothing whatsoever about self-selection QB.
“we examine the citation performance of author-choice open access”It is quite useful and interesting to examine citations for OA and non-OA articles where the OA is provided through (self-selected) “Author-Choice” (i.e., authors paying the publisher to make the article OA on the publisher’s website).
Most prior studies of the OA citation Advantage, however, are based on free self-archiving by authors on their personal, institutional or central websites. In the bigger studies, a robot trawls the web using ISI bibliographic metadata to find which articles are freely available on the web (Hajjem et al. 2005).
Hence a natural (indeed essential) control test that has been omitted from Davis’s current author-choice study – a test very much like the control test omitted from the Davis et al randomized OA study – is to identify the articles in the same sample that were made OA through author self-archiving. If those articles are identified and counted, that not only provides an estimate of the relative uptake of author-choice OA vs OA self-archiving in the same sample interval, but it allows a comparison of their respective OA Advantages. More important, it corrects the estimate of an OA Advantage based on author-choice OA alone: For, as Davis has currently done the analysis, any OA Advantage from OA self-archiving in this sample would in fact reduce the estimate of the OA Advantage based on author-choice OA (mistakenly counting as non-OA the articles and citation-counts for self-archived OA articles)
“METHODS… The uptake of the open access author-choice programs for these [11] journals ranged from 5% to 22% over the dates analyzed”Davis’s preprint does not seem to provide the data – either for individual journals or for the combined totals – on the percentage of author-choice OA (henceforth AC-OA) by year, nor on the relation between the proportion uptake of AC-OA and the size of the OA Advantage, by year.
As Davis has been careful to do multiple regression analyses on many of the article-variables that might correlate with citations and OA (article age, number of authors, number of references, etc.), it seems odd not to take into account the relation between the size of the AC-OA Advantage and the degree of uptake of AC-OA, by year. The other missing information is the corresponding data for self-archiving OA (henceforth SA-OA).
“[For] All of the journals… all articles roll into free access after an initial period [restricted to subscription access only for 12 months (8 journals), 6 months (2 journals) or 24 months (1 journal)]”(This is important in relation to the Early Access (EA) Advantage, which is the biggest contributor to the OA Advantage in the two cited studies by Kurtz on Astronomy. Astronomy has free access to the postprints of all articles in all astronomy journals immediately upon publication. Hence Astronomy has scope for an OA Advantage only through an EA Advantage, arising from the early posting of preprints before publication. The size of the OA Advantage in other fields -- in which (unlike in Astronomy) access to the postprint is restricted to subscribers-only for 6, 12, or 24 months -- would then be the equivalent of an estimate of an “EA Advantage” for those potential users who lack subscription access – i.e., the Accessibility Advantage, AA.)
“Cumulative article citations were retrieved on June 1, 2008. The age of the articles ranged from 18 to 57 months”Most of the 11 journals were sampled till December 2007. That would mean that the 2007 OA Advantage was based on even less than one year from publication.
“STATISTICAL ANALYSIS… Because citation distributions are known to be heavily skewed (Seglen, 1992) and because some of the articles were not yet cited in our dataset, we followed the common practice of adding one citation to every article and then taking the natural log”(How well did that correct the skewness? If it still was not normal, then citations might have to be dichotomized as a 0/1 variable, comparing, by citation-bracket slices, (1) 0 citations vs 1 or more citations, (2) 0 or 1 vs more than 1, (3) 2 or fewer vs. more than 2, (4) 3 or fewer vs. more than 3… etc.)
“For each journal, we ran a reduced [2 predictor] model [article age and OA] and a full [7 predictor] regression model [age, OA; log no. of authors, references, pages; Review; US author]”Both analyses are, of course, a good idea to do, but why was Journal Impact Factor (JIF) not tested as one of the predictor variables in the cross-journal analyses (Hajjem & Harnad 2007a)? Surely JIF, too, correlates with citations: Indeed, the Davis study assumes as much, as it later uses JIF as the multiplier factor in calculating the cost per extra citation for author-choice OA (see below).
Analyses by journal JIF citation-bracket, for example, can provide estimates of QA (Quality Advantage) if the OA Advantage is bigger in the higher journal citation-brackets. (Davis’s study is preoccupied with the self-selection QB bias, which it does not and cannot test, but it fails to test other candidate contributors to the OA Advantage that it can test.)
(An important and often overlooked logical point should also be noted about the correlates of citations and the direction of causation: The many predictor variables in the multiple regression equations predict not only the OA citation Advantage; they also predict citation counts themselves. It does not necessarily follow from the fact that, say, longer articles are more likely to be cited that article length is therefore an artifact that must be factored out of citation counts in order to get a more valid estimate of how accurately citations measure quality. One possibility is that length is indeed an artifact. But the other possibility is that length is a valid causal factor in quality! If length is indeed an artifact, then longer articles are being cited more just because they are longer, rather than because they are better, and this length bias needs to be subtracted out of citation counts as measures of quality. But if the extra length is a causal contributor to what makes the better articles better, then subtracting out the length effect simply serves to make citation counts a blunter, not a sharper instrument for measuring quality. The same reasoning applies to some of the other correlates of citation counts, as well as their relation to the OA citation Advantage. Systematically removing them all, even if they are not artifactual, systematically divests citation counts of their potential power to predict quality. This is another reason why citation counts need to be systematically validated against other evaluative measures [Harnad 2008a].)
“Because we may lack the statistical power to detect small significant differences for individual journals, we also analyze our data on an aggregate level”It is a reasonable, valid strategy, to analyze across journals. Yet this study still persists in drawing individual-journal level conclusions, despite having indicated (correctly) that its sample may be too small to have the power to detect individual-journal level differences (see below).
(On the other hand, it is not clear whether all the OA/non-OA citation comparisons were always within-journal, within-year, as they ought to be; no data are presented for the percentage of OA articles per year, per journal. OA/non-OA comparisons must always be within-journal/year comparisons, to be sure to compare like with like.)
“The first model includes all 11 journals, and the second omits the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), considering that it contributed nearly one-third (32%) of all articles in our dataset”Is this a justification for excluding PNAS? Not only was the analysis done with and without PNAS, but, unlike all the other journals, whose data were all included, for the entire time-span, PNAS data were only included from the first and last six months.
Why? PNAS is a very high impact factor journal, with highly cited articles. A study of PNAS alone, with its much bigger sample size, would be instructive in itself – and would almost certainly yield a bigger OA Advantage than the one derived from averaging across all 11 journals (and reducing the PNAS sample size, or excluding PNAS altogether).
There can be a QB difference between PNAS and non-PNAS articles (and authors), to be sure, because PNAS publishes articles of higher quality. But a within-PNAS year-by-year comparison of OA and non-OA that yielded a bigger OA Advantage than a within-journal OA/non-OA comparison for lower-quality journals would also reflect the contribution of QA. (With these data in hand, the author should not be so focused on confirming his hypotheses: take the opportunity to falsify them too!)
“we are able to control for variables that are well-known to predict future citations [but] we cannot control for the quality of an article”This is correct. One cannot control for the quality of an article; but in comparing within a journal/year, one can compare the size of the OA Advantage for higher and lower impact journals; if the advantage is higher for higher-impact journals, that favors QA over QB.
One can also take target OA and non-OA articles (within each citation bracket), and match the title words of each target article with other articles (in the same journal/year):
If one examines N-citation OA articles and N-citation non-OA articles, are their title-word-matched (non-OA) control articles equally likely to have N or more citations? Or are the word-matched control articles for N-citation OA articles less likely to have N or more citations than the controls for N-citation non-OA articles (which would imply that the OA has raised the OA article’s citation bracket)? And would this effect be greater in the higher citation brackets than in the lower ones (N = 1 to N = >16)?
If one is resourceful, there are ways to control, or at least triangulate on quality indirectly.
“spending a fee to make one’s article freely available from a publisher’s website may indicate there is something qualitatively different [about that article]”Yes, but one could probably tell a Just-So story either way about the direction of that difference: paying for OA because one thinks one's article is better, or paying for OA because one thinks one's article worse! Moreover, this is AC-OA, which costs money; the stakes are different with SA-OA, which only costs a few keystrokes. But this analysis omitted to identify or measure SA-OA.
“RESULTS…The difference in citations between open access and subscription-based articles is small and non-significant for the majority of the journals under investigation”(1) Compare the above with what is stated earlier: “Because we may lack the statistical power to detect small significant differences for individual journals, we also analyze our data on an aggregate level.”
(2) Davis found an OA Advantage across the entire sample of 11 journals, whereas the individual journal samples were too small. Why state this as if it were some sort of an empirical effect?
“where only time and open access status are the model predictors, five of the eleven journals show positive and significant open access effects.”(That does not sound too bad, considering that the individual journal samples were small and hence lacked the statistical power to detect small significant differences, and that the PNAS sample was made deliberately small!)
“Analyzing all journals together, we report a small but significant increase in article citations of 21%.”Whether that OA Advantage is small or big remains to be seen. The bigger published OA Advantages have been reported on the basis of bigger samples.
“Much of this citation increase can be explained by the influence of one journal, PNAS. When this journal is removed from the analysis, the citation difference reduces to 14%.”This reasoning can appeal only if one has a confirmation bias: PNAS is also the journal with the biggest sample (of which only a fraction was used); and it is also the highest impact journal of the 11 sampled, hence the most likely to show benefits from a Quality Advantage (QA) that generates more citations for higher citation-bracket articles. If the objective had not been to demonstrate that there is little or no OA Advantage (and that what little there is is just due to QB), PNAS would have been analyzed more closely and fully, rather than being minimized and excluded.
“When other explanatory predictors of citations (number of authors, pages, section, etc.) are included in the full model, only two of the eleven journals show positive and significant open access effects. Analyzing all journals together, we estimate a 17% citation advantage, which reduces to 11% if we exclude PNAS.”In other words partialling out 5 more correlated variables from this sample reduces the residual OA Advantage by 4%. And excluding the biggest, highest-quality journal’s data, reduces it still further.
If there were not this strong confirmation bent on the author’s part, the data would be treated in a rather different way: The fact that a journal with a bigger sample enhances the OA Advantage would be treated as a plus rather than a minus, suggesting that still bigger samples might have the power to detect still bigger OA Advantages. And the fact that PNAS is a higher quality journal would also be the basis for looking more closely at the role of the Quality Advantage (QA). (With less of a confirmation bent, OA Self-archiving, too, would have been controlled for, instead of being credited to non-OA.)
Instead, the awkward persistence of a significant OA Advantage even after partialling out the effects of so many correlated variables, despite restricting the size of the PNAS sample, and even after removing PNAS entirely from the analysis, has to be further explained away:
“The modest citation advantage for author-choice open access articles also appears to weaken over time. Figure 1 plots the predicted number of citations for the average article in our dataset. This difference is most pronounced for articles published in 2004 (a 32% advantage), and decreases by about 7% per year (Supplementary Table S2) until 2007 where we estimate only an 11% citation advantage.”(The methodology is not clearly described. We are not shown the percent OA per journal per year, nor what the dates of the citing articles were, for each cited-article year. What is certain is that a 1-year-old 2007 article differs from a 4-year-old 2004 article not just in its total cumulative citations in June 2008, but in that the estimate of its citations per year is based on a much smaller sample, again reducing the power of the statistic: This analysis is not based on 2005 citations to 2004 articles, plus 2006 citations to 2005 articles, plus 2007 citations to 2006 articles, etc. It is based on cumulative 2004-2008 citations to 2004, 2005, 2006 etc. articles, reckoned in June 2008. 2007 articles are not only younger: they are also more recent. Hence it is not clear what the Age/OA interaction in Table S2 really means: Has (1) the OA advantage for articles really been shrinking across those 4 years, or are citation rates for younger articles simply noisier, because based on smaller citation spans, hence (2) the OA Advantage grows more detectable as articles get older?)
From what is described and depicted in Figure 1, the natural interpretation of the Age/OA interaction seems to be the latter: As we move from one-year-old articles (2007) toward four-year-old articles, three things are happening: non-OA citations are growing with time, OA citations are growing with time, and the OA/non-OA Advantage is emerging with time.
“[To] calculate… the estimated cost per citation [$400 - $9000]… we multiply the open access citation advantage for each journal (a multiplicative effect) by the impact factor of the journal… Considering [the] strong evidence of a decline of the citation advantage over time, the cost…would be much higher…”Although these costs are probably overestimated (because the OA Advantage is underestimated, and there is no decline but rather an increase) the thrust of these figures is reasonable: It is not worth paying for AC-OA for the sake of the AC-OA Advantage: It makes far more sense to get the OA Advantage for free, through OA Self-Archiving.
Note, however, that the potentially informative journal impact factor (JIF) was omitted from the full-model multiple regression equation across journals (#6). It should be tested. So should the percentage OA for each journal/year. And after that the analysis should be redone separately for, say, the four successive JIF quartiles. If adding the JIF to the equation reduces the OA Advantage further, whereas without JIF the OA Advantage increases in each successive quartile, then that implies that a big factor in the OA Advantage is the Quality Advantage (QA).
“that we were able to explain some of the citation advantage by controlling for differences in article characteristics… strengthens the evidence that self-selection – not access – is the explanation for the citation advantage… more citable articles have a higher probability of being made freely accessible”Self-selection (QB) is undoubtedly one of the factors in the OA Advantage, but this analysis has not estimated the size of its contribution, relative to many other factors (AA, CA, DA, EA, QA). It has simply shown that some of the same factors that influence citation counts, influence the OA citation Advantage too.
By failing to test and control for the Quality Advantage in particular (by not testing JIFs in the full regression equation, by not taking percentage OA per journal/year into account, by restricting the sample-size for the highest impact, largest-sample journal, PNAS, by overlooking OA self-archiving and crediting it to non-OA, by not testing citation-brackets of JIF quartiles), the article needlessly misses the opportunity to analyze the factors contributing to the OA Advantage far more rigorously.
“earlier studies [on the OA Advantage] may be showing an early-adopter effect…”This is probably true. And early adopters also have a Competitive Advantage (CA). But with only about 20% OA being provided overall today, the CA is still there, except if it can be demonstrated – as Davis certainly has not demonstrated – that the c. 20% of articles that are being made OA today correspond sufficiently closely to that top 20% of articles that receive 80% of all citations. (Then the OA Advantage would indeed be largely QB.)
“authors who deposited their manuscripts in the arXiv tended to be more highly-cited than those who did not”There is some circularity in this, but it is correct to say that this correlation is compatible with both QB and QA, and probably both are contributing factors. But none of the prior studies nor this one actually estimate their relative contributions (nor those of AA, CA, DA and EA).
“any relative citation advantage that was enjoyed by early adopters would disappear over time”It is not that CA (Competitive Advantage) disappears simply because time elapses: CA only disappears if the competitors provide OA too! The same is true of QB (Quality Bias), which also disappears once everyone is providing OA. But at 20%, we are nowhere near 100% OA yet, hence there is plenty of scope for a competitive edge.
“If a citation advantage is the key motivation of authors to pay open access fees, then the cost/benefit of this decision can be quite expensive for some journals.”This is certainly true, and would be true even if the OA citation Advantage were astronomically big – but the reason it is true is that authors need not pay AC-OA fees for OA at all: they can self-archive for free (and indeed are being increasingly mandated by their funders and institutions to do so).
“Randomized controlled trials provide a more rigorous methodology for measuring the effect of access independently of other confounding effects (Davis et al., 2008)… the differences we report in our study… have more likely explained the effect of self-selection (or self-promotion) than of open access per se.”The syntax here makes it a little difficult to interpret, but if what is meant is that Davis et al’s prior study has shown that the OA Advantage found in the present study was more likely to be a result of QB than of QA, AA, CA, DA, or EA, then it has to be replied that that prior study showed nothing of the sort (Harnad 2008b). All it showed was that one cannot detect a significant OA Advantage at all one year after publication when OA is randomized. (The same is true when OA is not randomized.)
However, the prior Davis et al. study did find a significant DA (Download Advantage) for OA articles in the first year. And other studies have reported a significant correlation between early downloads and later citations (Brody et al. 2006).
So the prior Davis et al. study (1) confirmed the familiar failure to detect the OA Advantage in the first year, and (2) found a significant DA in the first year (probably predictive of a later OA citation Advantage). The present Davis study found (i) a significant OA Advantage, (ii) smallest in the first year (2007), much bigger by the fourth (2004).
“Retrospective analysis… our analysis is based on cumulative citations to articles taken at one point in time. Had we tracked the performance of our articles over time – a prospective approach – we would have stronger evidence to bolster our claim that the citation advantage is in decline. Still, we feel that cumulative citation data provides us with adequate inference.”Actually, it would be possible, with a fuller analysis using the ISI database, to calculate not only the citation counts for each cited article, but the dates of the citing articles. So a “prospective” analysis can be done in retrospect. Without performing that analysis, however, the present study does not provide evidence of a decline in the OA Advantage with time, just evidence of an improved signal/noise ratio for measuring the OA Advantage with time. A “prospective” analysis, taking citing dates as well as cited dates into account, would be welcome (and is far more likely to show that the size of the OA Advantage is, if anything, growing, rather than confirming the author’s interpretation, unwarranted on the present data, that it is shrinking).
“all of the journals under investigation make their articles freely available after an initial period of time [hence] any [OA Advantage] would be during these initial months in which there exists an access differential between open access and subscription-access articles. We would expect therefore that the effect of open access would therefore be strongest in the earlier years of the life of the article and decline over time. In other words, we would expect our trend (Figure 1) to operate in the reverse direction.”The reasoning here is a bit hard to follow, but the Kurtz studies that Davis cites show that in Astronomy, making preprints OA in the year or so before publication (after which all Astronomy postprints are OA) results in both “a strong EA effect and a strong [QB] effect.” But even in a fast-moving field like Astronomy, the effect is not immediate! There is no way to predict from the data for Astronomy how quickly an EA effect for nonsubscribers during the embargo year in Biomedicine should make itself felt in citations, but it is a safe bet that, as with citation latency itself, and the latency of the OA citation Advantage, the “EmA” (“Embargo Access”) counterpart of the EA effect in access-embargoed Biomedical journals will need a latency of a few years to become detectable. And since Davis’s age/OA interaction, based on static, cumulative, retrospective data, is just as readily interpretable as indicating that OA Advantages require time and sample-size growth in order to occur and be detected, the two patterns are perfectly compatible.
“we are at a loss to come up with alternative explanations to explain the monotonic decline in the citation advantage”There is no monotonic decline to explain. Just (a) low power in initial years, (b) cumulative data not analysed to equate citing/cited year spans, (c) the failure to test for QA citation-bracket effects, and (d) the failure to reckon self-archiving OA into the OA Advantage (treating it instead as non-OA).
If this had been a JASIST referee report, I would have recommended performing several further analyses taking into account:
and making the interpretation of the resultant findings more even-handed, rather than slanting toward the author’s preferred hypothesis that the OA Advantage is due solely or mostly to QB.(1) self-archiving OA
(2) percentage OA per journal per year
(3) JIFs and citation-brackets
(4) the full PNAS dataset
(5) citing-article-date vs cited-article-date
References
Full Disclosure: I am an OA advocate. And although I hope that I do not have a selective confirmation bias favoring QA, AA, CA, DA & EA, and against the Quality Bias (QB), I do think it is particularly important to ensure that QB is not given more weight than it has been empirically demonstrated to be able to bear.
Davis writes:"Free dissemination of the scientific literature may [1] speed up the transfer of knowledge to industry, [2] enable scientists in poor and developing countries to access more information, and [3] empower the general public. There are clearly many benefits to making one’s research findings freely available to the general public – a citation advantage may not be one of them."It may not be; but if it is not, then it must be demonstrated rigorously that it is not, both because of the prima facie evidence from download and citations, and because of what is at stake:
Currently, most researchers (c. 85%) are not yet providing OA to their research (Björk et al. 2008). Benefits [1]-[3] have clearly proven insufficient to motivate researchers to provide OA: only a small proportion of research articles have industrial applications [1] or general-public appeal [3], and most researchers are alas not motivated by charity to poor and developing countries [2]). Hence motivation to provide OA depends on other expected benefits.
Kurtz has suggested that QB itself may provide the motivation: seeing that the better research is being made OA by the better researchers should motivate all researchers to do likewise.
But on the assumption that the better researchers are making their better research OA for a reason, rather than just [1]-[3] (or just to imitate one another), it seems reasonable to ask what benefits their motivation is based on. And the enhancement of the uptake, usage, application and impact of their own research seems to be the obvious candidate. Otherwise, providing OA just for its own sake seems an irrational practice, especially on the part of the better researchers, for the better research.
A rigorous estimate of the true causal contribution of QB to the observed OA Advantage is also important for research policy reasons:
Although they have been cited in support of OA mandates by institutions and funders, industrial applications [1], charity [2] and public appeal [3] are not in themselves sufficient to motivate the adoption of such mandates, or compliance with them. Research impact itself would seem to be the natural rationale for maximizing research access.
So if the observed OA Advantage really does not provide the benefits that would motivate researchers to provide OA, this has to be demonstrated directly and rigorously. Why would the better researchers make their better research OA if it conferred no benefits (other than [1]-[3])? Too much is at stake to accept QB as the default hypothesis. The natural default hypothesis on the basis of the prima facie evidence (more downloads and citations) is that increasing the access to research increases the usage and impact of research. The higher download and citation counts correlated with OA support this. The burden of proof hence falls on providing evidence to the contrary.
Björk, Bo-Christer; Roosr, Annikki; Lauri, Mari (2008) Global annual volume of peer reviewed scholarly articles and the share available via different open access options. In: Chan, L. & Mornati, S. (Eds) ELPUB2008. Open Scholarship: Authority, Community, and Sustainability in the Age of Web 2.0 - Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Electronic Publishing Toronto, Canada 25-27 June 2008: pp. 178-186
Brody, T., Harnad, S. and Carr, L. (2006) Earlier Web Usage Statistics as Predictors of Later Citation Impact. Journal of the American Association for Information Science and Technology (JASIST) 57(8): 1060-1072
Craig, I. D., Plume, A. M., McVeigh, M. E., Pringle, J., & Amin, M. (2007). Do Open Access Articles Have Greater Citation Impact? A critical review of the literature. Journal of Informetrics 1(3): 239-248
Davis, P.M. (2008) Author-choice open access publishing in the biological and medical literature: a citation analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology (JASIST) (in press)
Davis, P. M., & Fromerth, M. J. (2007). Does the arXiv lead to higher citations and reduced publisher downloads for mathematics articles? Scientometrics 71(2): 203-215.
Davis, P. M., Lewenstein, B. V., Simon, D. H., Booth, J. G., & Connolly, M. J. L. (2008). Open access publishing, article downloads and citations: randomised trial. British Medical Journal 337: a586
Hajjem, C. and Harnad, S. (2007a) Citation Advantage For OA Self-Archiving Is Independent of Journal Impact Factor, Article Age, and Number of Co-Authors. Technical Report, Electronics and Computer Science, University of Southampton.
Hajjem, C. and Harnad, S. (2007b) The Open Access Citation Advantage: Quality Advantage Or Quality Bias? Technical Report, Electronics and Computer Science, University of Southampton
Hajjem, C., Harnad, S. and Gingras, Y. (2005) Ten-Year Cross-Disciplinary Comparison of the Growth of Open Access and How it Increases Research Citation Impact. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin 28(4) 39-47.
Harnad, S. (2007a) Craig et al.'s Review of Studies on the OA Citation Advantage. Open Access Archivangelism 248.
Harnad, S. (2007b) Where There's No Access Problem There's No Open Access Advantage Open Access Archivangelism 389
Harnad, S. (2008a) Validating Research Performance Metrics Against Peer Rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8 (11)
Harnad, S. (2008b) Davis et al's 1-year Study of Self-Selection Bias: No Self-Archiving Control, No OA Effect, No Conclusion British Medical Journal: Rapid Responses 337 (a568): 199775
Hitchcock, S. (2008) The effect of open access and downloads ('hits') on citation impact: a bibliography of studies
Kurtz, M. J., Eichhorn, G., Accomazzi, A., Grant, C., Demleitner, M., Henneken, E., et al. (2005). The effect of use and access on citations. Information Processing and Management 41: 1395-1402
Kurtz, M. J., & Henneken, E. A. (2007). Open Access does not increase citations for research articles from The Astrophysical Journal: Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
Lawrence, S. (2001) Free online availability substantially increases a paper's impactNature 31 May 2001
Moed, H. F. (2007). The effect of 'Open Access' upon citation impact: An analysis of ArXiv's Condensed Matter Section. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 58(13): 2047-2054
Seglen, P. O. (1992). The Skewness of Science. Journal of the American Society for Information Science 43(9): 628-638
Stevan Harnad
American Scientist Open Access Forum
Tuesday, August 12. 2008
Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Scholarly Performance Evaluation
 Ethics In Science And Environmental Politics (ESEP)
Ethics In Science And Environmental Politics (ESEP) ESEP Theme Section: The Use And Misuse Of Bibliometric Indices In Evaluating Scholarly Performance + accompanying Discussion Forum
Editors: Howard I. Browman, Konstantinos I. Stergiou
Quantifying the relative performance of individual scholars, groups of scholars, departments, institutions, provinces/states/regions and countries has become an integral part of decision-making over research policy, funding allocations, awarding of grants, faculty hirings, and claims for promotion and tenure. Bibliometric indices (based mainly upon citation counts), such as the h-index and the journal impact factor, are heavily relied upon in such assessments. There is a growing consensus, and a deep concern, that these indices — more-and-more often used as a replacement for the informed judgement of peers — are misunderstood and are, therefore, often misinterpreted and misused. The articles in this ESEP Theme Section present a range of perspectives on these issues. Alternative approaches, tools and metrics that will hopefully lead to a more balanced role for these instruments are presented.Browman HI, Stergiou KI INTRODUCTION: Factors and indices are one thing, deciding who is scholarly, why they are scholarly, and the relative value of their scholarship is something else entirely
ESEP 8:1-3
Campbell P Escape from the impact factor
ESEP 8:5-7
Lawrence PA Lost in publication: how measurement harms science
ESEP 8:9-11
Todd PA, Ladle RJ Hidden dangers of a ‘citation culture’
ESEP 8:13-16
Taylor M, Perakakis P, Trachana V The siege of science
ESEP 8:17-40
Cheung WWL The economics of post-doc publishing
ESEP 8:41-44
Tsikliras AC Chasing after the high impact
ESEP 8:45-47
Zitt M, Bassecoulard E Challenges for scientometric indicators: data demining, knowledge flows measurements and diversity issues
ESEP 8:49-60
Harzing AWK, van der Wal R Google Scholar as a new source for citation analysis
ESEP 8:61-73
Pauly D, Stergiou KI Re-interpretation of ‘influence weight’ as a citation-based Index of New Knowledge (INK)
ESEP 8:75-78
Giske J Benefitting from bibliometry
ESEP 8:79-81
Butler L Using a balanced approach to bibliometrics: quantitative performance measures in the Australian Research Quality Framework
ESEP 8:83-92
Erratum
Bornmann L, Mutz R, Neuhaus C, Daniel HD Citation counts for research evaluation: standards of good practice for analyzing bibliometric data and presenting and interpreting results
ESEP 8:93-102
Harnad S Validating research performance metrics against peer rankings
ESEP 8:103-107
« previous page
(Page 5 of 11, totaling 102 entries)
» next page
EnablingOpenScholarship (EOS)
Quicksearch
Syndicate This Blog
Materials You Are Invited To Use To Promote OA Self-Archiving:
Videos:
audio WOS
Wizards of OA -
audio U Indiana
Scientometrics -
The American Scientist Open Access Forum has been chronicling and often directing the course of progress in providing Open Access to Universities' Peer-Reviewed Research Articles since its inception in the US in 1998 by the American Scientist, published by the Sigma Xi Society.
The American Scientist Open Access Forum has been chronicling and often directing the course of progress in providing Open Access to Universities' Peer-Reviewed Research Articles since its inception in the US in 1998 by the American Scientist, published by the Sigma Xi Society.
The Forum is largely for policy-makers at universities, research institutions and research funding agencies worldwide who are interested in institutional Open Acess Provision policy. (It is not a general discussion group for serials, pricing or publishing issues: it is specifically focussed on institutional Open Acess policy.)
You can sign on to the Forum here.
Archives
Calendar
|
|
May '21 | |||||
| Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | ||||||
Categories
Blog Administration
Statistics
Last entry: 2018-09-14 13:27
1129 entries written
238 comments have been made


